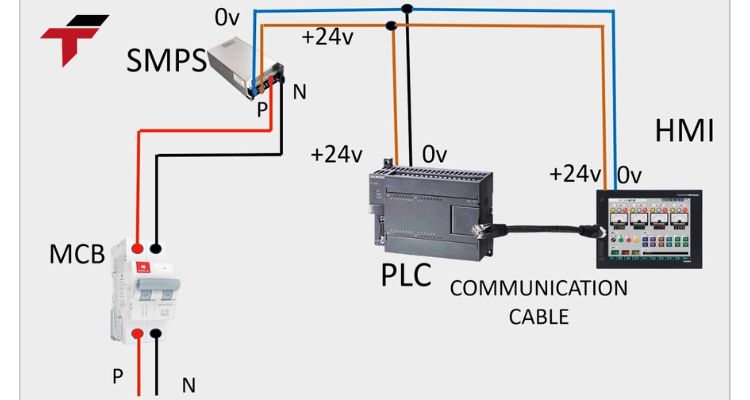
In an industrial automation environment, the Human-Machine Interface (HMI) and the Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) work hand in hand to ensure seamless operation and control.
The PLC acts as the brain of the system, collecting input data, processing it, and sending commands to field devices. Meanwhile, the HMI serves as the visual interface, allowing operators to monitor processes, view real-time data, and adjust parameters easily.
What Causes the HMI to Lose Connection with the PLC?
There are multiple potential causes for HMI–PLC communication failure. Identifying the root cause is essential to restoring the connection quickly. Common reasons include:
- Faulty Cables or Ports: Loose or damaged Ethernet/serial cables and defective switch ports often cause unstable or lost connections.
- Incorrect Network Configuration: When the HMI and PLC are not in the same subnet or share duplicate IP addresses, they cannot communicate properly.
- Protocol or Parameter Mismatch: Using an incompatible communication protocol or incorrect baud rate, parity, or stop bit setting can block data transfer.
- Configuration Errors in the HMI: Mistakes in tag mapping, driver selection, or outdated project files can cause invalid read/write requests.
- Firmware or Software Incompatibility: Outdated firmware versions or incompatible software can lead to miscommunication between devices.
- Power or Grounding Issues: Unstable power supplies or improper grounding can occasionally interrupt signal transmission.
What Causes the HMI to Lose Connection with the PLC?
How Can You Restore the Connection Between HMI and PLC?
When facing connection problems, a structured troubleshooting process helps minimize downtime. Follow these steps:
- Inspect Physical Connections: Ensure all Ethernet or serial cables are securely connected. Check for damaged connectors, defective ports, or faulty switches.
- Verify Network and IP Settings: Confirm both devices are assigned correct and unique static IP addresses within the same subnet.
- Check Protocol and Driver Settings: Ensure the HMI uses the correct communication driver (e.g., Modbus TCP vs. Modbus RTU) matching the PLC’s configuration.
- Restart the Devices: Reboot both HMI and PLC to clear potential communication stack errors.
- Update Firmware and Software: Install the latest firmware versions and ensure the configuration software is up to date.
- Use Diagnostic Tools: Employ tools like Wireshark or PLC/HMI diagnostic utilities to monitor data packets and identify connection bottlenecks.
If issues persist, contact the manufacturer’s technical support for deeper diagnostics or hardware replacement.
What Should You Keep in Mind to Prevent Future HMI-PLC Disconnections?
To ensure stable and reliable communication, consider these best practices:
- Design Redundant Communication Paths: Use dual Ethernet ports or redundant PLC communication modules to maintain connectivity during hardware failures.
- Select Industrial-Grade Components: Industrial switches, routers, and cables are more resistant to electrical noise, heat, and vibration.
- Perform Regular Maintenance: Periodically inspect connectors, cables, and ports for signs of wear or corrosion. Replace faulty components promptly.
- Enhance Network Security: Use VLANs, firewalls, and strong passwords to prevent unauthorized access or accidental configuration changes.
- Document and Backup Configurations: Keep backups of PLC and HMI programs to simplify recovery in case of a communication breakdown.

What Should You Keep in Mind to Prevent Future HMI-PLC Disconnections?
Why Is Maintaining a Stable HMI-PLC Connection So Important?
A reliable connection between HMI and PLC ensures:
- Continuous process monitoring
- Real-time control and quick response to faults
Reduced downtime and maintenance costs
Improved safety and operational efficiency
Disruptions in communication can lead to production delays, equipment failures, and potential safety risks. Therefore, maintaining a robust connection is crucial for any automation system.
Conclusion
HMI and PLC connectivity issues are a frequent challenge in industrial environments. However, with a solid understanding of how they communicate and a systematic troubleshooting approach, most problems can be resolved quickly.
By checking hardware connections, verifying configurations, and applying proactive maintenance, engineers can keep their automation systems running smoothly and prevent future communication failures.
Maintaining stable communication isn’t just a technical requirement — it’s the foundation of efficient, safe, and reliable industrial operations.


