The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is reshaping the landscape of industrial automation by integrating intelligent sensors, connected devices, and powerful data analytics. It builds upon the foundation of the Internet of Things (IoT) but is designed specifically for industrial environments such as manufacturing, logistics, and energy. Through IIoT, industries can connect machines, collect real-time data, and make smarter decisions that enhance productivity and safety.
One of the most visible areas of this transformation lies in the Human Machine Interface (HMI). Once static and limited, modern HMIs now act as dynamic control hubs that visualize and manage IIoT data serving as the bridge between human operators and smart industrial systems.
What Is IIoT and Why Does It Matter in Industrial Automation?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) refers to the interconnected network of industrial machines and devices that communicate via the internet to share data and improve operational performance. IIoT enables industries to digitize their operations, move toward predictive maintenance, and improve process visibility.
By connecting machines, sensors, and control systems, IIoT allows companies to monitor performance remotely, identify inefficiencies, and act before failures occur – a key step toward achieving Industry 4.0 standards.
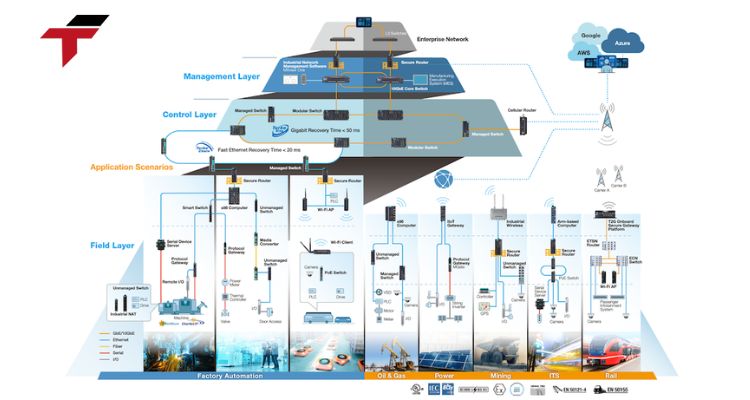
What Is IIoT and Why Does It Matter in Industrial Automation?
What Are the Core Features That Define IIoT?
IIoT introduces a suite of advanced features that revolutionize how factories operate, analyze data, and manage assets.
- Remote Monitoring and Control: IIoT allows operators to access live dashboards via web-based or cloud HMIs, minimizing the need for physical presence on-site.
- Predictive Maintenance: By analyzing vibration, temperature, and energy data, IIoT systems can forecast potential breakdowns, preventing costly downtime.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: IIoT collects and processes massive data streams, presenting them through HMIs as clear insights that help optimize processes and enhance safety.
- Scalability and Flexibility: IIoT systems can expand from a single line to a large-scale factory network, integrating seamlessly with existing infrastructure through HMI gateways.
- Edge and Cloud Integration: By combining edge computing for immediate responses and cloud systems for large-scale analytics, IIoT ensures ba alance between speed and intelligence.
How Does IIoT Transform the Role of HMIs?
IIoT doesn’t just enhance machine communication — it fundamentally changes how operators interact with industrial systems through HMIs.
- From Static Screens to Smart Interfaces: Modern HMIs powered by IIoT feature real-time visualizations, custom KPIs, and interactive dashboards that improve operator engagement.
Continuous Real-Time Data: With IIoT, HMIs receive live data feeds, allowing operators to monitor performance, detect anomalies, and respond to alerts instantly. - Enhanced Security and User Access: IIoT-enabled HMIs implement user authentication, encryption, and role-based control to protect critical systems from unauthorized access.
- Smarter Maintenance and Troubleshooting: HMIs can now display machine histories, diagnostic insights, and recommended repair actions automatically — reducing manual intervention.

How Does IIoT Transform the Role of HMIs?
What Factors Should Be Considered When Integrating IIoT with HMIs?
While the integration of IIoT and HMI creates immense value, success depends on careful system design and security planning.
- Protocol Compatibility: Verify that the HMI supports industrial communication protocols such as OPC UA, MQTT, Modbus TCP, or Ethernet/IP.
- Edge vs. Cloud Deployment: Choose between edge computing for low-latency control or cloud analytics for broad data visibility and scalability.
- Cybersecurity Strategy: Implement robust defenses such as firewalls, VPNs, and intrusion detection systems to safeguard IIoT networks.
- Efficient Data Management: Develop a data strategy covering storage, visualization, and retention to handle the vast volume of IIoT data effectively.
- System Interoperability: Ensure seamless integration between HMI, SCADA, MES, and ERP systems to achieve unified factory intelligence.
How Is IIoT Different from IoT?
Although IIoT and IoT share similar concepts — connected devices and data analytics — their applications and priorities differ dramatically.
| Feature | IoT (Consumer) | IIoT (Industrial) |
| Data Volume | Moderate | Extremely High |
| Reliability | Medium Priority | Mission-Critical |
| Latency Tolerance | Seconds | Milliseconds |
| Protocols | Wi-Fi, Bluetooth | OPC UA, MQTT, Modbus |
| Primary Use | Smart homes, gadgets | Manufacturing, logistics, energy |
In essence, IIoT emphasizes real-time performance, reliability, and scalability, while IoT focuses on convenience and personalization.
Conclusion
The fusion of IIoT and HMI is shaping the next generation of industrial control systems. With intelligent visualization, real-time analytics, and secure connectivity, IIoT-driven HMIs empower factories to operate with higher efficiency, reduced downtime, and smarter decision-making.
As industries continue their digital transformation, the convergence of IIoT and HMI will no longer be an innovation, it will be the new foundation of Industry 4.0-ready automation.


