Robotic Process Automation (RPA) helps businesses automate repetitive, rule-based tasks, improving efficiency, accuracy, and productivity across departments. This guide by Flextech covers how RPA works, its types, benefits, common use cases, challenges, and best practices to help organizations optimize processes and drive digital transformation.
What Is Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
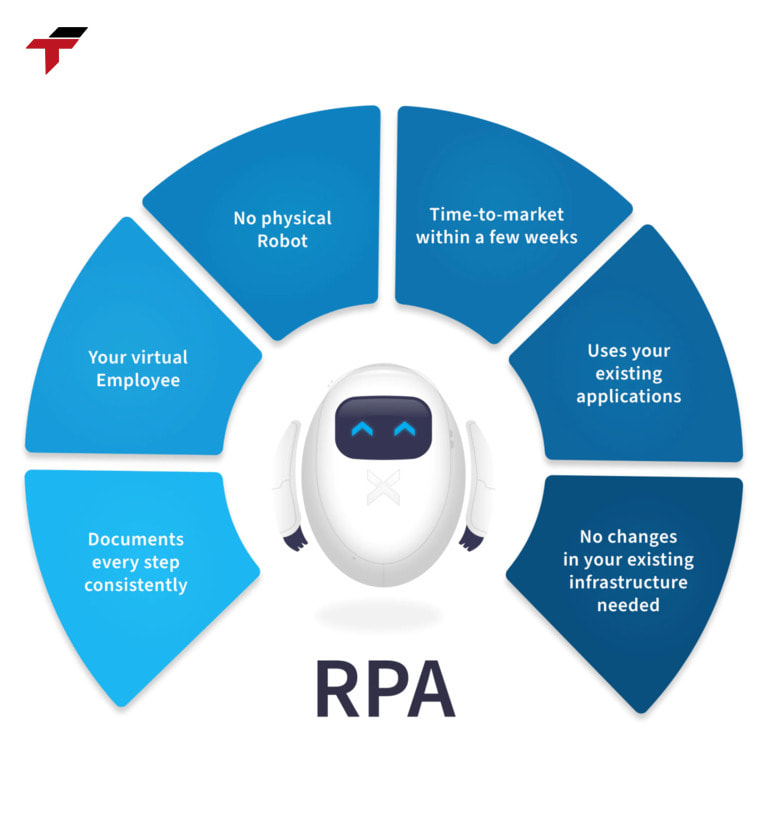
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is a technology that uses software robots, also known as “bots,” to automate repetitive, rule-based tasks that are traditionally performed by humans. These tasks often involve interacting with digital systems, such as data entry, transaction processing, report generation, and form filling.
Unlike traditional automation, which often requires extensive system integration, programming, or changes to underlying software, RPA works at the user interface level. This means it can operate within existing systems without requiring major modifications, making implementation faster, more flexible, and cost-effective.
Key Components of RPA:
- Software Robots (Bots): The digital workers that perform tasks automatically by interacting with applications and systems.
- Automation Platforms: Tools and software suites that enable the creation, deployment, and management of bots.
- Integration Modules: Features that allow bots to connect to different systems like ERP, CRM, databases, and web applications without requiring API-level changes.
3 Key Components of RPA
How Does RPA Work?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) operates by simulating human actions in digital systems to perform repetitive, rule-based tasks efficiently and accurately. The workflow can be broken down into 8 steps:
Step 1: Identify Processes for Automation
- Analyze business workflows to determine which tasks are suitable for automation.
- Ideal tasks are repetitive, rule-based, high-volume, and prone to human error.
- Establish clear objectives for what the RPA implementation should achieve, such as reducing processing time, minimizing errors, or freeing up employees for higher-value work.
Step 2: Map the Workflow
- Document each step of the task, including decision points, inputs, outputs, and exceptions.
- Define rules and conditions that the bot must follow.
- This mapping ensures the bot executes tasks accurately and consistently.
Step 3: Configure and Develop the RPA Bot
- Use an RPA platform to create the bot according to the workflow.
- Assign the actions the bot should perform, such as logging in to applications, copying data, entering information, or generating reports.
- Set exception handling procedures to ensure the bot can manage errors or unexpected situations.
Step 4: Test the Bot in a Controlled Environment
- Run the bot in a test environment to validate its performance.
- Monitor for errors, workflow gaps, or unexpected behavior.
- Adjust the bot’s configuration to optimize efficiency and accuracy.
Step 5: Deploy the Bot
- Launch the bot in the live production environment.
- Ensure it can operate alongside employees and existing systems without disrupting daily operations.
- Monitor initial performance closely to confirm that it meets expected objectives.
Step 6: Process Execution and Integration
- The bot performs tasks automatically, interacting with applications, databases, and other systems just like a human operator would.
- Common integrations include:
- ERP Systems: Automating order processing, inventory updates, or invoice handling.
- CRM Systems: Managing customer records, updating contact details, and generating reports.
- Databases and Spreadsheets: Extracting, transforming, and loading data across multiple sources.
Step 7: Logging, Reporting, and Monitoring
- The bot maintains a log of all actions for auditing and compliance purposes.
- Generate reports to highlight completed tasks, exceptions, or errors requiring human intervention.
- Continuous monitoring allows managers to track efficiency and identify opportunities for further optimization.
Step 8: Continuous Improvement and Scaling
- Analyze performance metrics to improve bot workflows and reduce processing time further.
- Scale automation by adding more bots to handle additional tasks or processes.
- Integrate RPA with AI and machine learning for intelligent automation, enabling bots to handle unstructured data, make decisions, and adapt to process changes.
By following these steps, RPA streamlines business operations, reduces manual errors, enhances productivity, and integrates seamlessly with existing systems, providing a reliable and scalable approach to digital process automation.

The workflow can be broken down into 8 steps
What Are the Key Benefits of Implementing RPA?
Implementing Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers a wide range of benefits for businesses across industries. 5 key advantages include:
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: RPA bots can execute repetitive tasks much faster than humans, working continuously without breaks. This significantly accelerates workflows and allows organizations to process higher volumes of tasks in less time.
- Reduced Errors and Improved Accuracy: Bots follow predefined rules consistently, eliminating human errors caused by fatigue, oversight, or manual data entry. This ensures higher data accuracy and reduces the need for rework.
- Cost Savings and Operational Optimization: By automating routine tasks, businesses can reduce labor costs, minimize delays, and optimize resource allocation. Over time, the investment in RPA generates measurable cost savings and operational efficiency.
- Enhanced Compliance and Auditability: RPA bots maintain detailed logs of all actions performed, providing clear audit trails for regulatory compliance. Automated processes reduce the risk of non-compliance due to manual mistakes.
- Freeing Human Employees for Higher-Value Tasks: By handling repetitive and mundane tasks, RPA allows employees to focus on strategic, analytical, or creative work, enhancing overall workforce productivity and satisfaction.
5 Key Benefits of Implementing RPA
Which Business Processes Can Be Automated Using RPA?
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) can be applied across multiple business functions to streamline operations, reduce manual effort, and improve efficiency. It is especially effective for tasks that are repetitive, rule-based, and high-volume. Here are 4 common use cases:
How Can RPA Improve Finance and Accounting Operations?
RPA is highly effective in finance and accounting departments where accuracy and speed are critical. Tasks that can be automated include:
- Invoice Processing: Bots can automatically extract data from invoices, validate it against purchase orders, and enter it into accounting systems.
- Accounts Payable/Receivable: RPA can manage payment approvals, generate reminders, and post transactions.
- Reconciliations: Bots compare records across multiple systems to identify discrepancies, reducing human errors.
- Report Generation: Financial reports can be automatically compiled, formatted, and delivered to stakeholders on schedule.
By automating these processes, finance teams save time, reduce errors, and maintain better compliance with financial regulations.
How Can RPA Transform Human Resources Tasks?
In HR, RPA helps manage administrative tasks efficiently, allowing employees to focus on strategic initiatives. Key applications include:
- Employee Onboarding: Bots handle repetitive onboarding processes such as account creation, document verification, and training assignment.
- Payroll Automation: RPA ensures timely and accurate payroll processing by collecting data, calculating salaries, and generating payslips.
- Benefits Administration: Enrollment, updates, and record-keeping for employee benefits can be automated.
- Leave Management: Bots can manage leave requests, approvals, and record updates across HR systems.
Automation reduces administrative burden, accelerates HR workflows, and improves employee experience.
How Can RPA Enhance Customer Service?
Customer service departments often face high volumes of repetitive tasks, which can be automated using RPA:
- Handling Repetitive Queries: Bots can respond to common questions via email, chat, or ticketing systems.
- Form Processing: Data entry and validation from customer forms can be automated.
- Updating Records: Customer profiles, transaction histories, and contact information can be updated automatically across systems.
- Ticket Management: Bots can categorize, prioritize, and assign tickets, ensuring faster resolution.
This not only speeds up response times but also allows human agents to focus on complex or high-value customer interactions.
How Can RPA Support IT and Operations?
RPA is increasingly used in IT and operational departments to ensure smooth and efficient system management:
- System Monitoring: Bots can continuously monitor IT systems, applications, and networks for issues.
- Report Generation: Routine operational reports can be automatically compiled and delivered to management.
- Automating Backups: RPA ensures scheduled backups are performed accurately and consistently.
- Routine Maintenance Tasks: Software updates, data validation, and system health checks can be handled by bots.
What Are the Challenges and Limitations of Implementing RPA?
While Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offers significant benefits, organizations need to be aware of potential challenges to implement it successfully and maximize its value.
- Initial Implementation Cost and Complexity: Deploying RPA requires investment in software, infrastructure, and skilled personnel. Proper planning and thorough process mapping are essential to avoid inefficiencies and ensure the automation delivers real benefits.
- Maintenance and Bot Governance: RPA bots need continuous monitoring, updates, and management to function correctly. Changes in business processes or systems can disrupt bot performance, and poor governance can lead to errors, downtime, or compliance risks.
- Scalability Issues: RPA works best with standardized and well-documented workflows. If processes vary significantly or are not clearly defined, scaling automation across the organization can be challenging and may reduce overall efficiency.
- Risks of Over-Automation: Automating too many processes without proper evaluation can introduce unnecessary complexity, decrease flexibility, and create dependency on bots. Over-automation may also increase the likelihood of errors if exceptions are not handled effectively.
By understanding these limitations, businesses can plan and manage RPA implementations strategically, ensuring that automation enhances productivity, reduces errors, and provides long-term operational value.

Challenges and Limitations of Implementing RPA
What is the difference between workflow automation and RPA?
Similarly
- Both aim to automate business processes to increase productivity, reduce errors, and save costs.
- Both focus on processes that are repetitive, have clear rules, and do not require much human judgment.
Different
| Workflow Automation | RPA Automation | |
| Scope of Automation | Automation of entire business processes, suitable for streamlining a series of related tasks. | Suitable for discrete, repetitive, rule-based tasks such as data entry. |
| Complexity | Typically more complex, may involve multiple systems, applications, and data. | Simpler, focused on specific tasks, and can be easily deployed. |
| Flexible | More flexible, can adapt to many different types of processes. | Flexible, can adapt to many different types of processes. |
| Human Interaction | Users must make decisions for complex tasks or special cases. | Minimize human intervention |
| Related Technology | Often relies on process management tools such as BPM. (Business Process Management). | Incorporate artificial intelligence (AI) or machine learning to enhance automation. |
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is no longer just a technological trend—it is a powerful tool that transforms the way businesses operate. By automating repetitive, rule-based tasks, RPA helps organizations increase efficiency, reduce errors, lower operational costs, and free employees to focus on higher-value work.
At Flextech, we specialize in delivering tailored RPA solutions that integrate seamlessly with your existing systems. Our team of experts helps businesses identify the right processes to automate, implement efficient RPA workflows, and maximize the value of digital transformation initiatives.


