Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing the way businesses operate, offering smarter automation, data-driven insights, and innovative solutions across multiple industries. From healthcare and finance to manufacturing and retail, AI enables organizations to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences. This guide explores how AI works, its key types, practical applications, benefits, challenges, and best practices to help businesses harness the full potential of this transformative technology.
What Is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) refers to the simulation of human intelligence in machines that are programmed to think, learn, and perform tasks typically requiring human cognition. AI systems can process data, recognize patterns, make decisions, and improve performance over time, enabling automation of complex processes and problem-solving across various domains.
- Algorithms: The set of rules and mathematical models that guide AI systems to analyze data and make decisions.
- Data: High-quality, structured, and unstructured datasets are essential for training AI models to recognize patterns and make accurate predictions.
- Computing Power: AI systems require significant processing capabilities to handle large volumes of data and perform complex computations efficiently.
How Does AI Work?
AI works by analyzing data, learning patterns, and making intelligent decisions. Understanding its workflow—from data collection to model training, prediction, and continuous improvement—helps businesses leverage AI effectively. The following 4 steps break down the AI workflow into clear, actionable stages.
Step 1: Data Collection and Preprocessing
The first step in AI is gathering large volumes of data from multiple sources, such as databases, sensors, IoT devices, or online platforms. This raw data often contains inconsistencies, duplicates, or irrelevant information.
Preprocessing cleans, organizes, and formats the data to ensure it is accurate and suitable for training AI models. High-quality, well-prepared data is crucial for achieving reliable and precise AI outcomes.
Step 2: Training Models Using Machine Learning or Deep Learning
After preprocessing, AI systems use machine learning or deep learning algorithms to train models. Machine learning analyzes structured data, identifying patterns and correlations, while deep learning handles unstructured data like images, text, and audio.
During training, models adjust their internal parameters to reduce errors and improve accuracy, enabling the AI system to make better predictions or decisions.
Step 3: Decision-Making and Predictions
Once trained, AI models can process new data and make decisions or predictions based on learned patterns. This step allows AI to perform tasks such as forecasting customer behavior, detecting anomalies, recommending products, or assisting with medical diagnoses. The system applies the insights gained from historical data to deliver actionable results in real time.
Step 4: Continuous Learning and Adaptation
Advanced AI systems continuously learn from new data and feedback, refining their models over time. This adaptive capability allows AI to improve accuracy, respond to changing conditions, and handle complex or dynamic environments. Continuous learning ensures that the AI system remains effective and relevant as business needs and data evolve.
What Are the Different Types of AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be categorized based on its capabilities and level of intelligence. Understanding 3 types helps businesses and individuals recognize the potential applications and limitations of AI systems.
Narrow AI (Weak AI)
Narrow AI, also known as Weak AI, is designed to perform specific tasks within a limited domain. It cannot operate outside its defined functions and does not possess general intelligence. Most AI applications in use today fall into this category.
Key Characteristics of Narrow AI:
- Specialized for a single task or a set of closely related tasks
- Operates based on pre-defined rules and data patterns
- Cannot adapt or think beyond its programming
- Examples: virtual assistants like Siri or Alexa, recommendation engines, spam filters
General AI (Strong AI)
General AI, or Strong AI, refers to systems with human-like intelligence capable of understanding, learning, and applying knowledge across a wide range of tasks. Unlike Narrow AI, Strong AI can reason, plan, and solve problems in unfamiliar situations.
Key Characteristics of General AI:
- Capable of learning and reasoning like a human
- Can apply knowledge to different domains
- Exhibits problem-solving, decision-making, and planning abilities
- Still largely theoretical; no fully functional General AI exists yet
Superintelligent AI
Superintelligent AI represents a hypothetical future level of AI that surpasses human intelligence in all aspects, including creativity, problem-solving, and social intelligence. It is considered the ultimate goal of AI research but also raises significant ethical and safety concerns.
Key Characteristics of Superintelligent AI:
- Outperforms humans in every cognitive task
- Able to improve its own algorithms autonomously
- Can potentially innovate and solve complex global challenges
- Currently theoretical and not yet realized
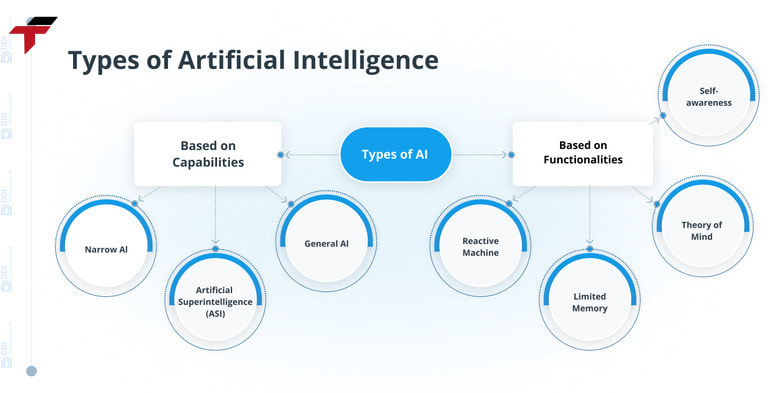
3 types of AI helps businesses and individuals recognize the potential applications
What Are the Benefits of Implementing AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings transformative advantages to businesses by automating processes, analyzing large datasets, and enabling smarter decision-making.
- Increased Efficiency and Productivity: AI can perform repetitive and time-consuming tasks faster than humans, allowing employees to focus on higher-value work. This results in shorter processing times, faster operations, and improved overall productivity.
- Improved Accuracy and Decision-Making: AI reduces human error and delivers precise, data-driven insights. By analyzing patterns and trends from vast datasets, AI helps businesses make more informed decisions and minimize risks.
- Cost Reduction and Operational Optimization: Automating routine tasks and optimizing processes reduces labor costs and operational inefficiencies. AI also helps companies allocate resources more effectively and eliminate redundant workflows.
- Enhanced Customer Experience: AI-powered tools, such as chatbots, recommendation engines, and personalized services, improve customer engagement and satisfaction by providing faster, accurate, and tailored responses.
- Scalability of Operations: AI can handle large volumes of data and tasks simultaneously, allowing businesses to scale operations without proportional increases in workforce or resources.
- Predictive Capabilities: AI can analyze historical data to predict trends, customer behavior, or potential issues, enabling proactive decision-making and risk management.
- Innovation and Competitive Advantage: By leveraging AI for insights, automation, and optimization, companies can innovate faster, develop new products or services, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
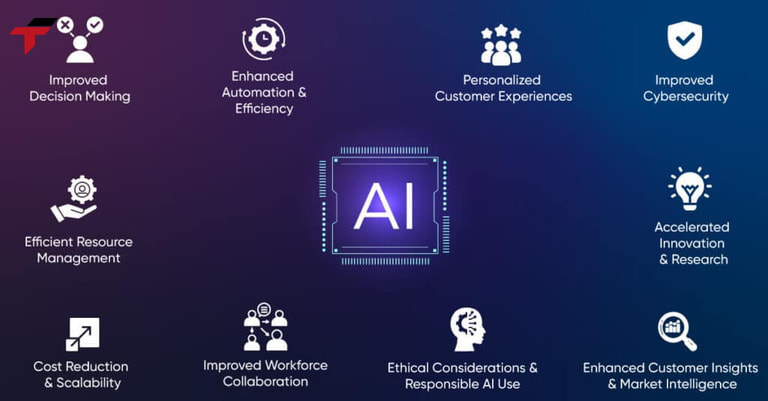
Artificial Intelligence (AI) brings transformative advantages to businesses by automating processes
What Are the Challenges and Limitations of AI?
While AI offers significant benefits, its implementation comes with challenges that must be carefully managed. Organizations face concerns such as data privacy, algorithmic bias, high costs, and technical complexity. Ensuring high-quality data and ethical oversight is essential to maximize AI’s value and avoid potential risks.
- Data Privacy and Security Concerns: AI systems rely heavily on large amounts of data, raising concerns about data protection, privacy compliance, and potential security breaches.
- High Implementation Costs and Technical Complexity: Developing and deploying AI solutions requires investment in infrastructure, software, and skilled personnel, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
- Bias in AI Algorithms and Ethical Issues: AI systems may inherit biases from historical data or flawed training processes, leading to unfair outcomes or ethical dilemmas in decision-making.
Dependence on Data Quality and Availability: AI performance depends on accurate, complete, and high-quality data. Poor or insufficient data can compromise the effectiveness and reliability of AI systems.
What Are the Best Practices for Implementing AI?
Implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) successfully requires more than just deploying technology—it demands careful planning, strategic execution, and ongoing management. To maximize benefits and minimize risks, organizations should follow several best practices:
- Define Clear Objectives and ROI: Before implementing AI, it is essential to identify specific business goals and desired outcomes. Establish measurable key performance indicators (KPIs) to track success, such as increased efficiency, cost savings, or improved customer satisfaction.
- Ensure High-Quality Data: Data is the foundation of any AI system. Organizations must collect, clean, and organize datasets to ensure they are accurate, consistent, and representative. High-quality data improves model training, enhances predictive accuracy, and reduces the risk of biased or unreliable outputs.
- Combine AI with Human Oversight: While AI can automate complex tasks, human supervision remains crucial. Humans should validate outputs, manage exceptions, and provide context for decisions that AI alone cannot interpret. This hybrid approach balances automation with accountability and reduces potential errors.
- Continuous Monitoring and Model Updates: AI models are not static; they require ongoing monitoring to ensure consistent performance. Regularly retraining models with new data, adjusting algorithms for evolving conditions, and auditing results are critical to maintaining accuracy, relevance, and reliability over time.

Implementing Artificial Intelligence (AI) successfully requires more than just deploying technology
In which industries is Artificial Intelligence (AI) commonly applied?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a wide range of applications across industries, transforming how businesses operate, make decisions, and interact with customers. From automating routine tasks to providing advanced insights, AI is increasingly used to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance innovation in multiple sectors. The following industries illustrate where AI has the most significant impact today.
Healthcare
AI is transforming the healthcare industry by enabling faster, more accurate diagnoses, enhancing surgical precision, and providing personalized patient care.
- Diagnostic imaging: AI analyzes X-rays, MRIs, CT scans to detect diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease or tissue damage, often with greater accuracy than doctors.
- Robots for surgery: Surgical robots such as Da Vinci, controlled by AI, help perform complex surgeries with absolute precision.
- Personalized healthcare applications: AI is integrated into smart wearable devices (smartwatches) to monitor heart rate, sleep, and activity levels, and provide timely health advice.
Transportation
AI is revolutionizing the transportation industry by enabling autonomous vehicles and optimizing logistics. Intelligent systems can recognize obstacles, make navigation decisions, and determine the most efficient routes, improving safety, reducing costs, and enhancing delivery efficiency.
- Self-driving cars: AI technology in self-driving cars (like Tesla) allows for the recognition of obstacles, traffic signs, and automatic navigation decisions.
- Optimizing logistics transportation: AI determines the shortest and most efficient routes, reducing delivery times and costs. For example, companies like FedEx or DHL use AI to manage delivery routes.
Manufacturing
In manufacturing, AI enhances precision, efficiency, and predictive capabilities. From AI-powered robotic arms to predictive maintenance systems, these technologies streamline production processes, reduce downtime, and optimize resource allocation.
- Industrial robots: AI-powered robotic arms can perform tasks like welding, cutting, or assembling with greater precision than humans.
- Predictive maintenance: AI analyzes historical data to predict when equipment needs maintenance, reducing downtime and optimizing costs.
Education
AI is transforming education by personalizing learning and supporting educators. Intelligent tutoring systems, automated grading, and data-driven insights help tailor lessons to individual student needs, improving learning outcomes and teaching efficiency.
- Education chatbots: AI helps students answer questions, suggest study materials, and help manage study time effectively.
- Platforms like Khan Academy or Duolingo use AI to tailor lessons to each student’s ability and learning speed.
AI has been present in almost every field, from manufacturing, healthcare, education, to agriculture and entertainment. With continuous advancements, artificial intelligence continues to open up huge potential to improve efficiency, productivity, and experiences in life and work.
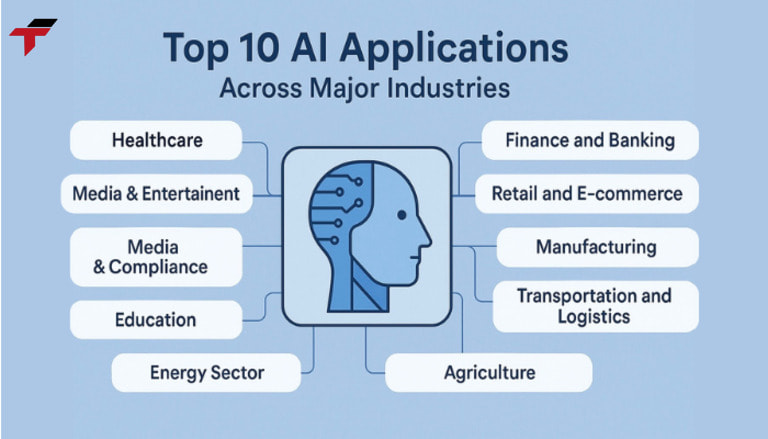
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has a wide range of applications across industries
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer just a futuristic concept—it is a transformative technology that is reshaping industries, optimizing operations, and enhancing decision-making across healthcare, finance, manufacturing, retail, education, transportation, and IT.
At Flextech, we specialize in providing advanced AI solutions tailored to your business needs. From implementing intelligent automation and predictive analytics to integrating AI-powered tools into your operations, Flextech helps organizations harness the full potential of AI. Partnering with us ensures not only cutting-edge technology but also strategic guidance to maximize ROI, streamline processes, and drive sustainable growth.


