Input/Output (I/O) interfaces are essential components in industrial automation, enabling PLCs to receive signals from sensors and control machines accurately. From digital and analog I/O to local and remote modules, these interfaces play a vital role in connecting devices, ensuring efficient data flow, and supporting smart factory operations. In this guide, we explore the types, applications, selection criteria, and best practices for I/O interfaces, helping businesses optimize automation systems and improve overall productivity with Flextech solutions.
What is Input /Output Interface ?
An Input/Output (I/O) Interface is the component that enables data exchange between a controller’s internal memory and external devices. In PLC systems, it plays a crucial role by receiving signals from the environment (Input) and sending control commands to actuators or machines (Output). This mechanism ensures that automated processes on production lines operate accurately, consistently, and efficiently.
The operation of an I/O Interface typically includes three main stages:
- Input Interface – Collecting signals from devices: At this stage, the system gathers signals from peripheral components and converts them into voltage or current values that the CPU can interpret. Examples include push buttons, object detection sensors, temperature sensors, and limit switches.
- Signal Processing – CPU analyzes and evaluates data: The CPU processes the received data using predefined PLC programs written in languages such as Ladder Logic, Structured Text, and others. Based on this logic, the processor determines the appropriate response or action.
- Output Interface – Sending control signals to external equipment: After processing, the CPU delivers output commands to devices such as relays, indicator lights, motors, or control valves. These actions help execute the required operations in the automation system.
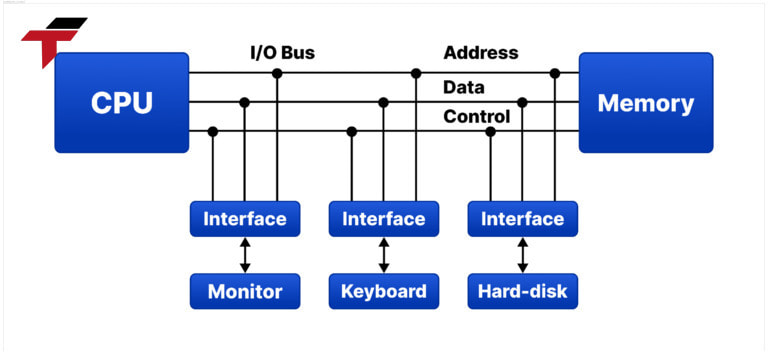
The operation of an I/O Interface typically includes three main stages
Why is Input/Output Interface important?
In automation systems, Input/Output Interface (I/O Interface) plays an extremely important role because it is the bridge between the PLC controller and peripheral devices. Without I/O Interface, the PLC will not be able to receive data from sensors or switches, nor will it be able to send control signals to devices such as motors, relays or indicator lights.
Therefore, I/O Interface helps the automation system operate smoothly, accurately, and efficiently. In this article, we will learn why I/O Interface is indispensable in the process of controlling and monitoring industrial applications.
- Helps automate the operating process: This helps minimize human errors, increase efficiency and maintain stability in operation.
- Reduce the processing load on the CPU: By pre-processing the input signal, Input/Output Interface helps reduce the direct workload on the PLC’s CPU. This increases the performance and efficiency of the system.
- Scalability: I/O Interface allows the PLC system to easily expand the number of inputs/outputs and integrate with new devices without changing the entire system structure.
- Ability to integrate with industrial networks: I/O Interface is often designed to integrate with industrial networks such as Profibus, Ethernet/IP, Modbus, making it easy to connect and exchange data with other systems in the factory. This ensures continuity and synchronization throughout the entire production process.
- Ensuring high accuracy and consistency: Signals are processed using high-level programming languages such as Ladder Logic, Structure text, Function Block Diagram (FBD) … to ensure accuracy and reliability during operation.
Input/Output Interface (I/O Interface) plays an extremely important role
How many types of input/output interfaces are there?
Input/Output interfaces in PLC systems come in a variety of forms, each designed to support different signal types, connection methods, and application requirements. Understanding these classifications helps engineers select the most suitable I/O configuration for efficient, stable, and scalable automation systems.
Classification by signal type
When selecting an I/O interface for a PLC system, the first and most fundamental classification is based on the type of signal the device needs to process. Each signal type serves a different purpose and directly affects how the PLC interprets and controls the system. In general, I/O interfaces can be divided into two main categories:
- Digital I/O: Receives binary signals (ON/OFF, 1/0). This is a simple signal with two states, often used in on/off applications.
- Analog I/O: Receives analog (continuous) signals from sensors such as temperature sensors, pressure sensors, current sensors. The signal is usually in the form of voltage (0-10V) or current (4-20mA).
These signal types play a crucial role in determining the accuracy, level of control, and overall responsiveness of an automation system.
Classification by connection method
Another way to categorize I/O interfaces is based on how they connect to the PLC system. The connection method directly impacts installation complexity, communication speed, and the system’s flexibility. Typically, I/O interfaces are divided into two main types:
- Wired I/O: This is a traditional connection method through physical wires.
- Wireless I/O: Uses wireless protocols such as Zigbee, Wi-Fi, or Bluetooth to transmit signals.
Each connection method offers different advantages depending on the environment and system requirements.
Based on connection form
I/O interfaces can also be classified by how they are physically arranged and connected to the PLC system. This classification affects scalability, installation flexibility, and the overall architecture of the control system. There are two common connection forms:
- Local I/O: I/O modules are directly connected to the PLC, often mounted in the same rack or frame.
- Remote I/O: I/O modules are located remotely and connected to the PLC via network protocols such as Ethernet/IP, Profibus, or Modbus. This allows for easy system expansion and reduces wiring costs.
Classification by number of channels
I/O interfaces can also be grouped based on the number of input/output points they provide. This classification helps determine the scalability, density, and suitability of the module for specific automation tasks. Generally, there are two main types:
- Discrete I/O: Designed to connect individual input/output devices. Discrete I/O primarily handles binary signals with two states ON (1) or OFF (0).
- Modular I/O: Integrates multiple I/O channels into one module, saving space and making them easy to replace when needed. Modular I/O can handle both digital and analog signals, and is often designed for easy expansion.
Choosing the right I/O Interface type depends on the specific needs of the application and operating environment. By understanding the types of I/O Interfaces and their characteristics, you can optimize your PLC system for maximum efficiency and reliability.
Input/Output interfaces in PLC systems come in a variety of forms
What Are the Applications of I/O Interfaces in Industry?
Input/Output interfaces are essential in connecting PLCs and other control systems with the physical world. They are widely applied across many industrial sectors:
- Manufacturing: I/O interfaces control machinery, manage conveyor systems, operate robotic arms, and enable automated assembly lines. They ensure precise, real-time control of production processes.
- IIoT and Smart Factories: In smart factories, I/O modules collect real-time data from sensors and equipment. This data supports predictive maintenance, process optimization, and integration with Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) platforms.
- Energy: I/O interfaces monitor electrical systems, control power distribution, and manage renewable energy systems. They help maintain system stability and prevent downtime.
- Automotive, Logistics, and Robotics: From automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to warehouse robotics and automotive production lines, I/O modules provide critical signal input and control output for safe and efficient operation.
How to Choose the Right I/O Interface?
Selecting the right Input/Output (I/O) interface is a critical step in designing a reliable and efficient automation system. A careful choice ensures accurate data collection, smooth control of devices, and the ability to expand the system in the future. Several 4 key factors should be considered when making this decision.
- Signal Type: The type of signal the I/O interface needs to handle is one of the first considerations. Digital I/O is suitable for simple ON/OFF signals, such as switches, push buttons, or relay controls.
- Connection Method: The method of connection between the I/O interface and the PLC can significantly affect system performance. Wired I/O provides stable, interference-resistant communication, making it ideal for harsh industrial environments with high electromagnetic noise.
- Number of Channels and System Layout: Another crucial factor is the number of input and output points required by the system. Discrete I/O is appropriate for smaller setups with fewer devices, while modular I/O allows multiple channels to be integrated into a single module, saving space and enabling easier maintenance.
- Environmental Conditions and Standards: Industrial environments often present challenges such as high temperatures, humidity, vibration, and electromagnetic interference. I/O interfaces should be chosen based on their ability to withstand these conditions.
4 key factors should be considered when making this decision
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Input/Output Interface
1. Do I/O signals need isolation?
Yes, signal isolation is often essential in industrial environments. Isolation separates the input/output circuits from the PLC CPU or other sensitive electronics, protecting them from voltage spikes, electrical noise, and potential faults. This ensures accurate signal transmission, prevents equipment damage, and enhances the overall reliability of the automation system.
2. Can PLC I/O modules be expanded?
Yes, many PLC systems are designed with modularity in mind. Modular I/O allows additional channels to be added easily without replacing the entire system. Remote I/O can also be installed at different locations and connected via industrial communication protocols such as Ethernet/IP or Modbus. This flexibility supports system growth, reduces downtime during upgrades, and accommodates increasing automation needs.
3. What are the advantages of remote I/O over local I/O?
Remote I/O offers several benefits in large or distributed industrial setups. It reduces the amount of wiring needed, which saves installation time and cost. Remote I/O modules can be placed closer to field devices, minimizing signal loss and improving reliability. Additionally, it simplifies system expansion and maintenance, as new modules can be added or replaced without affecting the central PLC rack. Remote I/O also enables better scalability for smart factory and IIoT applications.
Conclusion
Input/Output Interface is an important component in the PLC system, ensuring accurate communication between the controller and peripheral devices. The effective design and operation of this interface will help optimize the performance of the automation system, from the production line to the energy monitoring system.
Flextech provides advanced I/O interface solutions tailored for industrial automation and smart factory environments. Our products include digital and analog I/O modules, local and remote I/O systems, and wired or wireless connectivity options, designed to meet high industrial standards for reliability and scalability. With Flextech, businesses can optimize automation systems, enhance productivity, and seamlessly integrate I/O interfaces with PLCs and IIoT platforms.


