Rotary encoders are fundamental electromechanical devices in the world of industrial automation. Installed within specialized motors, their primary function is to determine the exact position and velocity of objects accurately. They are widely adopted across various automation sectors, including critical applications like assembly lines and specialized labeling equipment.
Known for their outstanding features, rotary encoders are capable of continuous rotation at a full 360-degree free angle, enabling them to observe and track objects with high accuracy. Given their affordability and high applicability, these devices are a valuable asset for any modern production facility.
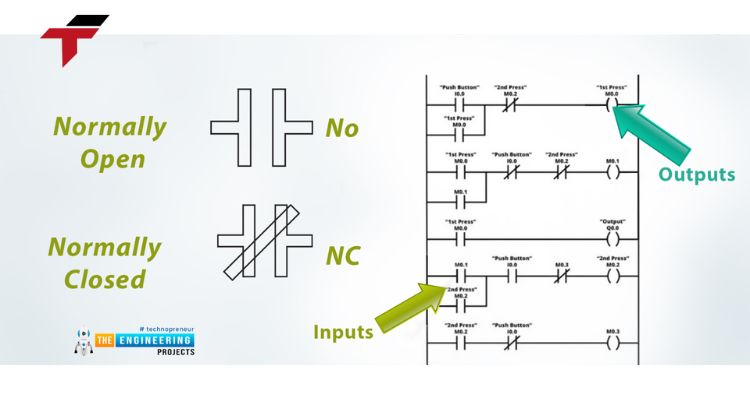
What is the primary use of a rotary encoder?
Rotary encoders are commonly employed for monitoring and control purposes. In industrial automation, they are extensively used for direction transmission and speed control.
A key application is providing motor feedback to precisely control the speed of a transmission shaft. This makes them indispensable in machinery such as high-speed labeling machines, advanced textile equipment, and other systems requiring accurate motion control.

What is the primary use of a rotary encoder?
Main Types and Classifications of Rotary Encoders
While there are many specific models of rotary encoders, they are broadly categorized into three main types based on their operating principles and output:
Incremental Encoders
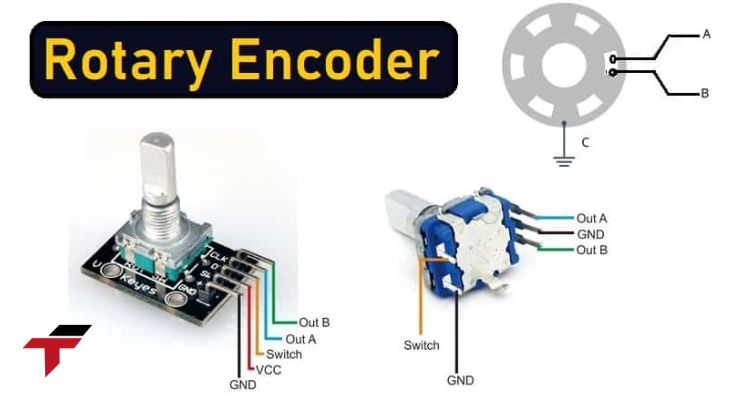
- Function: These devices convert the rotational movement of a shaft into a series of electrical pulses to determine the direction and angle of rotation.
- Mechanism: They can operate using optical, magnetic, or mechanical principles.
- Output: They typically provide two output signals (A and B) that are electrically offset from each other. This offset allows the control system to determine the direction of rotation.
Absolute Encoders
- Function: Absolute encoders are crucial for locating, adjusting, and synchronizing rotating parts within machinery. They are designed to provide the precise position information of the shaft.
- Key Advantage: Unlike incremental types, an absolute encoder retains its position information regardless of the state of rotation or rest. This makes them vital components in automation systems focused on precise speed and position control.
Linear Encoders
- Function: Unlike the previous two rotational types, linear encoders are specifically used to encode linear movements.
- Application: They accurately measure and control the position, movement, and speed of an object traveling along a straight axis. They play a significant role in applications that require precise control over linear motion.
Main Types and Classifications of Rotary Encoders
Common Reasons for Rotary Encoder Failure
Like any piece of industrial equipment, rotary encoders can encounter issues that compromise their operating efficiency. Understanding these common problems is essential for preventative maintenance:
- Bent Shaft: The encoder shaft must be perfectly straight for optimal operation. A bent shaft creates excessive pressure on the internal bearing, which can lead to thermal overload and eventual failure.
- Environmental Influence: Operation in harsh environments is a frequent cause of damage. Places with excessive dust, debris, or sudden, dramatic temperature changes can easily affect the internal components and reduce the device’s lifespan.
- Signal Problems: Issues with the output signal are common and often stem from poor installation, electrical interference, or an internal short circuit within the wiring.
Common Reasons for Rotary Encoder Failure
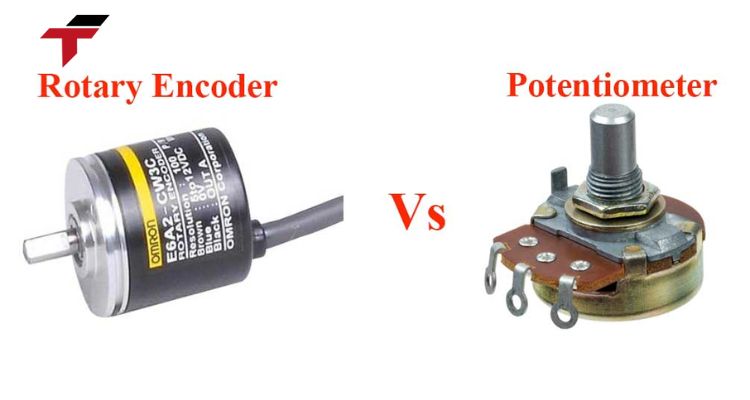
Rotary Encoders vs. Potentiometers: A Comparison
While both devices are used in control systems, their function, structures, and outputs are fundamentally different.
| Feature | Rotary Encoders | Potentiometers |
| Operation Angle | Continuous operation in both directions (360 degrees) | Limited to rotation at a specific, fixed angle |
| Setup Complexity | More complex setup required | Easy setup and integration |
| Internal Structure | Rotating shaft, encoder disc, phototransistor, and signal processing circuit | Positive/negative voltage connections and a movable slider (acts as a voltage divider) |
| Precision | High-precision control and seamless integration with digital systems | Requires continuous control; offers relative precision |
| Signal Type | Uses a digital signal (pulses or binary code) | Uses an analog signal (variable voltage) |
| Approximate Cost | Around $20 – $70 | Around $20 |
Where to Acquire Quality Rotary Encoders
The market offers a wide variety of rotary encoders across different classifications and price points. It is crucial to select a supplier that guarantees genuine products to avoid purchasing poor-quality items that will affect your automation system’s reliability.
Choosing a reputable supplier like Flextech ensures absolute confidence in your purchase. They typically commit to:
- Providing 100% genuine products with verifiable origin documents.
- Offering a comprehensive 12-month warranty and support for fast delivery.
- Often providing added services like free installation and transportation within a defined service area.
- Maintaining a team of professional staff ready to advise on the most suitable solution for specific technical needs and budgets.
For reliable products and expert consultation, contact a trusted provider immediately to support your automation requirements.