Communication ports are essential for modern industrial automation, connecting devices, sensors, PLCs, and control systems to ensure seamless data exchange. From factory automation to IIoT integration, choosing the right communication port is crucial for operational efficiency, reliability, and real-time monitoring. This guide explores the types, applications, challenges, and best practices for communication ports in industrial environments, helping businesses make informed decisions and optimize their smart factory systems with Flextech solutions.
What Are Communication Ports in Industrial Automation?
Communication ports are essential interfaces that allow industrial devices, PLCs, computers, and sensors to exchange data efficiently. In industrial automation, these ports serve as the backbone of machine-to-machine (M2M) communication, enabling control systems to monitor, analyze, and manage manufacturing processes in real time.
Without reliable communication ports, data transfer between devices would be slow, error-prone, or even impossible, limiting the performance of automated systems.
Communication ports can be physical or virtual. Physical ports include traditional serial ports like RS-232 or RS-485, USB, and Ethernet connections. Virtual ports, on the other hand, are software-defined and often used for industrial applications that require remote monitoring, simulation, or data logging.
Each type of port is designed to handle specific data transmission needs, such as speed, distance, and signal integrity.
How Do Communication Ports Work?
Communication ports in industrial automation serve as the bridge between devices, allowing data to flow reliably and efficiently. Their operation can be broken down into 6 steps:
Step 1: Data Generation
Devices such as sensors, PLCs, and actuators generate data that needs to be transmitted. This data can include measurements, control signals, or status updates. The type of data depends on the device and the industrial process it monitors or controls.
Step 2: Data Encoding and Formatting
Before transmission, data is encoded into a suitable format according to the communication protocol being used (e.g., RS-232, Modbus, Ethernet/IP). This ensures that the receiving device can correctly interpret the incoming signals. Encoding also helps prevent errors during transmission and maintains data integrity.
Step 3: Data Transmission
The formatted data is transmitted from the sending device through the communication port. Depending on the port type, this can happen via:
- Serial communication: Data is sent one bit at a time over RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485 connections.
- Parallel communication: Multiple bits are sent simultaneously (less common in modern industrial systems).
- Ethernet or network communication: Data packets are sent over wired or wireless networks.
Step 4: Signal Reception
The receiving device’s communication port detects incoming signals and extracts the transmitted data. Proper reception depends on signal quality, transmission distance, and the compatibility of the communication protocol.
Step 5: Data Decoding and Processing
Once received, the data is decoded back into a usable format. The device then processes this information according to the programmed instructions, such as adjusting motor speeds, opening valves, or logging sensor readings into a database.
Step 6: Feedback and Acknowledgment (Optional)
In some systems, the receiving device sends an acknowledgment back to the sender to confirm successful transmission. This ensures reliable communication and allows error-checking or retransmission if necessary.
Communication ports are fundamental to industrial automation, enabling devices to exchange critical information in real time, optimize processes, and integrate seamlessly with systems like IIoT, SCADA, and smart factory platforms. Choosing the right type of port ensures faster, safer, and more reliable industrial communication.
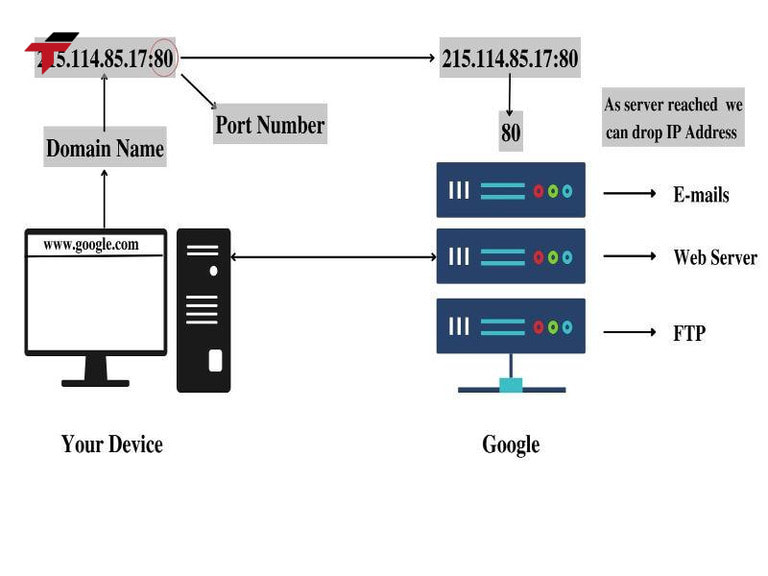
Their operation can be broken down into 6 steps
What Types of Communication Ports Are Commonly Used?
In industrial automation, communication ports are essential for connecting devices, transferring data, and enabling machine-to-machine (M2M) communication. Selecting the right type of port depends on factors such as distance, data rate, reliability, and application environment. The most commonly used communication ports include:
Serial Ports: RS-232, RS-422, RS-485
Serial ports are widely used in industrial devices due to their simplicity and reliability for long-distance data transmission.
- RS-232: Common for short-distance, point-to-point communication. It’s easy to implement but limited in distance (up to ~15 meters) and data speed.
- RS-422: Supports longer distances and faster data rates compared to RS-232, suitable for multi-drop connections with higher noise immunity.
- RS-485: Ideal for industrial networks, allowing multiple devices to communicate on the same bus over long distances (up to 1200 meters). RS-485 is robust, cost-effective, and widely used in PLCs, sensors, and actuators.
Ethernet Ports: RJ45, Industrial Ethernet
Ethernet ports provide high-speed, reliable, and standardized communication for modern industrial networks.
- RJ45: Standard connector used for both office and industrial Ethernet applications. Supports data transfer up to 1 Gbps for most industrial needs.
- Industrial Ethernet: Designed for harsh environments, these ports use reinforced connectors, shielded cables, and support protocols like EtherNet/IP, Profinet, or Modbus TCP. They offer high reliability, long-distance communication, and easy integration with IIoT systems.
USB Ports
USB ports are often used for programming PLCs, transferring data, or connecting peripheral devices. They are convenient for short-term connections and easy configuration. USB supports fast data transfer rates and is compatible with a wide range of industrial devices, making it ideal for maintenance, updates, and data logging.
Wireless Ports: Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, Zigbee, LoRa
Wireless communication ports enable flexibility and remote connectivity in industrial environments.
- Wi-Fi: Provides high-speed data transfer over medium distances, suitable for IIoT applications or wireless HMI connections.
Bluetooth: Short-range communication ideal for mobile devices, handheld sensors, or maintenance tools. - Zigbee & LoRa: Low-power, long-range wireless protocols used for sensors, monitoring systems, and distributed automation networks. They are particularly useful in large factories or remote installations where cabling is impractical.
Choosing the right communication port depends on your application requirements, environmental conditions, and data transmission needs. Using the appropriate port ensures reliable device communication, reduces downtime, and enables seamless integration with smart factory systems and IIoT platforms.
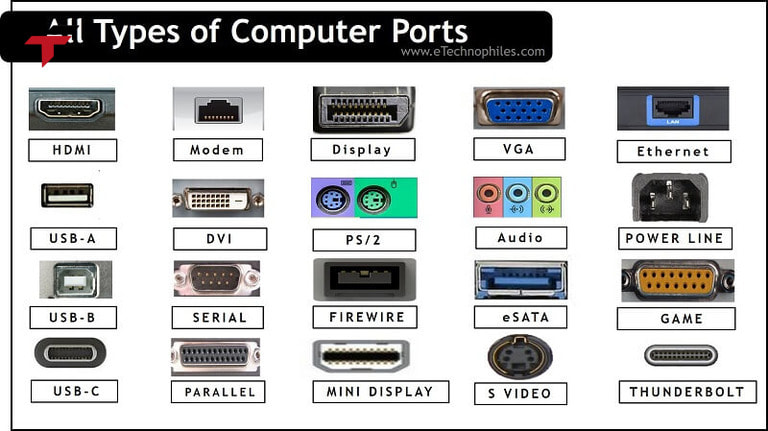
4 Types of Communication Ports
What are the considerations when selecting and using Communication Ports?
Choosing and using the right type of communication ports (Communication Ports) in PLC is a decisive factor for the performance and stability of the automation system. Here are some important considerations that you need to consider:
- Number of connected devices: If you need to connect many devices, scalable ports such as Ethernet or Fieldbus buses are a good choice.
- Data transmission speed: Depending on the scale of the enterprise system. For example, Ethernet is suitable for real-time communication and large data, while low speeds such as RS-232 or RS-485 are enough for simple systems. Choosing the wrong speed can cause delays or waste resources.
- Scalability and integration: Choose a communication port that supports easy expansion for future projects.
- Operating environment: If the working environment has high electromagnetic interference, choose ports with good anti-interference capabilities.
- Reputable supplier: Currently, there are many units selling Communication Ports on the market, so businesses need to be wise in choosing.
5 considerations when selecting and using Communication Ports
What Are the Applications of Communication Ports in Industry?
Communication ports are the backbone of modern industrial systems, providing reliable pathways for data exchange between devices, machines, and centralized control systems. Their applications span multiple sectors and play a vital role in enabling automation, efficiency, and real-time monitoring.
- Factory Automation and Machine-to-Machine (M2M) Communication: Communication ports connect PLCs, sensors, actuators, and other industrial devices, allowing machines to exchange data in real time. This facilitates precise control over production lines, reduces human error, and increases overall efficiency.
- Remote Monitoring and IIoT Integration: In smart factories and IIoT ecosystems, communication ports transmit data from devices to cloud platforms or central monitoring systems. This enables predictive analytics, remote diagnostics, and real-time decision-making, helping businesses optimize operations without being physically present on-site.
- Data Logging, Control Systems, and Predictive Maintenance: Ports allow devices to continuously send operational data to SCADA systems, historians, or databases. This enables detailed performance tracking, early detection of equipment issues, and predictive maintenance strategies that reduce downtime and extend machinery life.
- Robotics, Automotive, and Logistics Systems: In robotics and automated logistics, communication ports ensure coordinated movements, real-time tracking, and synchronization of processes. In automotive manufacturing, they facilitate precise control over assembly lines, vehicle testing, and quality assurance operations.
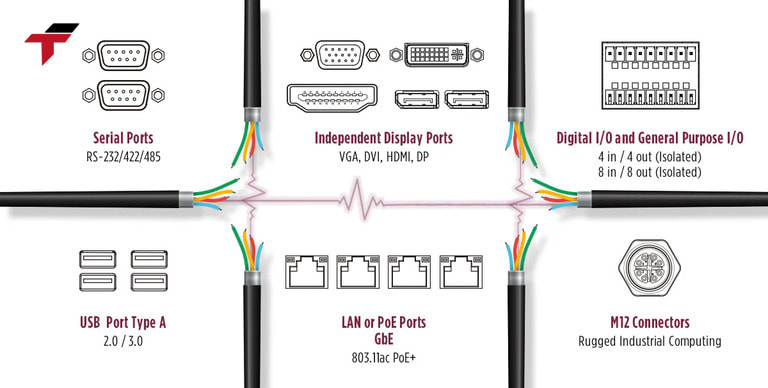
Their applications span multiple sectors and play a vital role in enabling automation
What Are the Challenges and Limitations of Communication Ports?
While communication ports are critical for industrial automation, they also come with specific challenges that can impact performance, reliability, and security:
- Signal Interference and Noise: Electrical noise from motors, welders, or other industrial equipment can disrupt data transmission, causing errors or miscommunication. Proper shielding, grounding, and filtering are essential to maintain signal integrity.
- Distance Limitations and Data Loss: Each communication port has a maximum transmission range. Exceeding this distance without repeaters or proper cabling can result in slow communication, data loss, or system malfunctions.
- Compatibility and Protocol Issues: Industrial devices often use different protocols (Modbus, Profibus, EtherNet/IP). Ensuring compatibility between devices and ports is crucial; otherwise, communication errors or integration challenges can occur.
- Security and Cybersecurity Risks: Communication ports connected to networks can become vulnerable entry points for cyberattacks. Industrial systems must implement strong security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and access controls, to protect sensitive operational data.
By understanding these challenges, businesses can select appropriate ports, design reliable networks, and implement protective measures, ensuring smooth and secure industrial communication.
Conclusion
Communication ports are a fundamental component of industrial automation, enabling reliable data exchange between devices, PLCs, sensors, and control systems. They play a crucial role in factory automation, IIoT integration, robotics, logistics, and predictive maintenance.
By understanding the types, applications, and challenges of communication ports, businesses can optimize their industrial networks, improve operational efficiency, and ensure seamless integration with modern smart factory technologies.
At Flextech, we provide a comprehensive range of industrial-grade communication solutions, including wired and wireless ports, serial and Ethernet interfaces, and scalable systems designed for harsh industrial environments. With our expertise, businesses can implement reliable, secure, and high-performance communication networks, empowering their digital transformation journey and enhancing competitiveness in the Industry 4.0 era.


