In industrial automation, knowing the right terms is essential to optimize processes and work efficiently. Understanding these core concepts helps professionals navigate the fast-evolving world of smart manufacturing. In this article, Flextech highlights 10 must-know terms that form the foundation of industrial automation knowledge.
Automation
Automation is the implementation of technology, machines, and control systems to carry out tasks or processes without requiring direct human intervention. It allows industrial systems to operate continuously, consistently, and efficiently, replacing manual labor for repetitive, dangerous, or complex tasks.
- Increased Productivity: Automated systems can operate 24/7, significantly increasing output compared to manual labor.
- Reduced Human Error: Replacing repetitive human tasks with machines reduces mistakes caused by fatigue or oversight.
- Cost Efficiency: Automation lowers labor costs, reduces material waste, and optimizes energy consumption.
- Improved Precision and Quality: Automated processes maintain consistent quality standards and improve product accuracy.
- Enhanced Flexibility: Modern automation systems can be reprogrammed or adjusted for new products or production changes, providing adaptability in dynamic manufacturing environments.
Programmable Logic Controller – PLC
PLC (Programmable Logic Controller) is an important device in industrial automation, used to control and monitor manufacturing processes. PLCs can be programmed to perform logic tasks, such as turning equipment on and off, controlling motors, and processing signals from sensors.
- Continuous and Reliable Operation: PLCs provide 24/7 monitoring and control with minimal downtime.
- Reduced Human Dependency: Automates repetitive or dangerous tasks, allowing workers to focus on higher-value operations.
- Increased Process Stability: Ensures consistent quality and performance, reducing errors and variability.
- Scalable and Flexible: Easily programmable to adapt to new production requirements or process modifications.
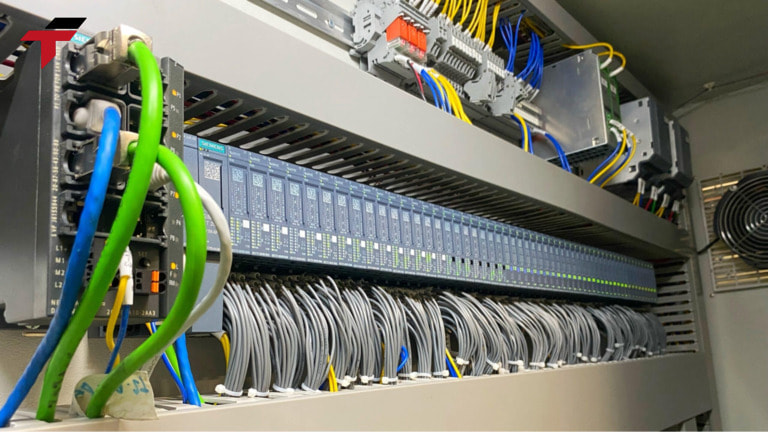

Programmable Logic Controller – PLC
Distributed Control System – DCS
A DCS system is a distributed control system, used to manage and monitor complex industrial processes. DCS differs from PLCs in that it is designed to control large-scale systems, such as chemical plants, power plants, or large-scale manufacturing systems.
- Improved Reliability and Stability: Distributed control reduces the risk of total system failure and allows localized troubleshooting.
- Scalable Architecture: Easy to expand by adding new controllers or subsystems without major redesigns.
- Optimized Process Efficiency: Provides precise control over complex operations, minimizing waste and energy consumption.
- Centralized Monitoring: Operators can oversee the entire plant from a central control room while still maintaining local control at each subsystem.
- Enhanced Safety and Compliance: Continuous monitoring ensures processes stay within safe and regulatory limits.
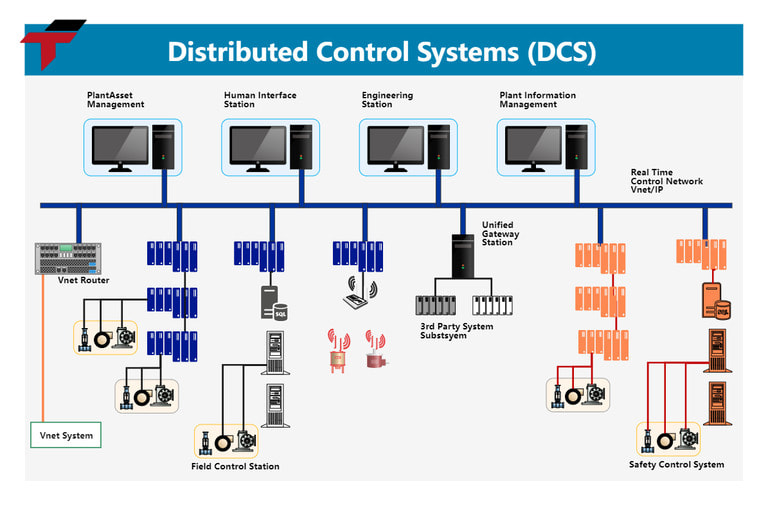
Distributed Control System – DCS
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition – SCADA
SCADA is a supervisory control and data acquisition system, used to monitor and control processes remotely. SCADA allows managers to monitor the status of systems, detect problems, and adjust automated equipment without having to be physically present on site.
- Enhanced Operational Efficiency: Provides operators with centralized, real-time data to make informed decisions.
- Improved Safety and Reliability: Alerts and automated interventions reduce the risk of accidents and system downtime.
- Data-Driven Insights: Historical data analysis supports process optimization, preventive maintenance, and compliance reporting.
- Remote Accessibility: Operators can monitor and control multiple sites without being physically present, reducing labor and travel costs.
- Scalability: SCADA systems can grow with the organization, supporting additional sensors, devices, and sites over time.
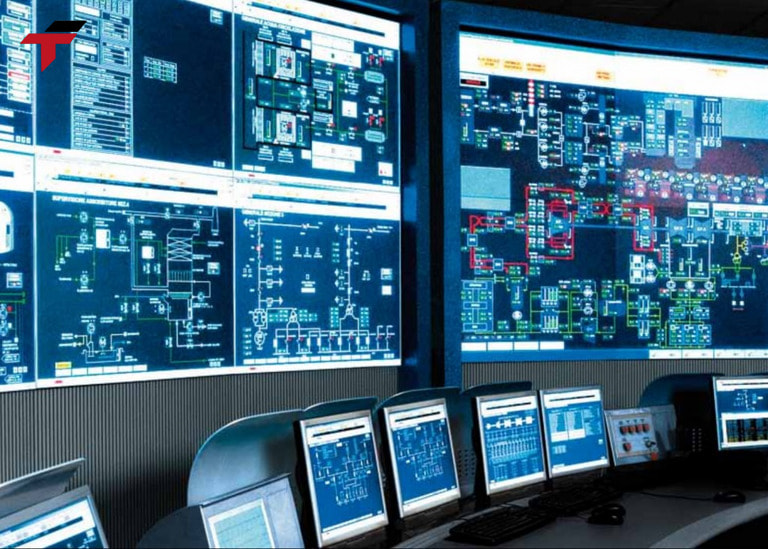

Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition – SCADA
Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are automated devices that can perform tasks such as welding, assembling, or quality control in a manufacturing environment. These robots can operate independently or in coordination with other devices in an automation system.
Thanks to their ability to work accurately and continuously, industrial robots help increase productivity, reduce errors, and improve safety in the work environment. Common applications of robots in manufacturing include automating assembly, product inspection, and packaging.
Automation Control Systems
Automated control systems are the brains of automated manufacturing processes. These systems can use simple logic controllers (ON/OFF) or more complex control systems such as PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) to regulate factors such as temperature, pressure, and flow rate during the manufacturing process.
Automated control systems help minimize human intervention, improving accuracy and consistency in the final product.
Industrial Internet of Things -IIoT
IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is a concept that describes the connection of devices, sensors, and machines in a network to collect, analyze, and share data. IIoT provides remote monitoring and control capabilities, helping to improve efficiency and reduce downtime in the manufacturing process.
- Increased Productivity: Optimizes operations and reduces manual interventions.
- Enhanced Equipment Reliability: Predictive maintenance minimizes unplanned breakdowns.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Real-time insights enable smarter management of industrial operations.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces energy consumption, maintenance costs, and operational inefficiencies.
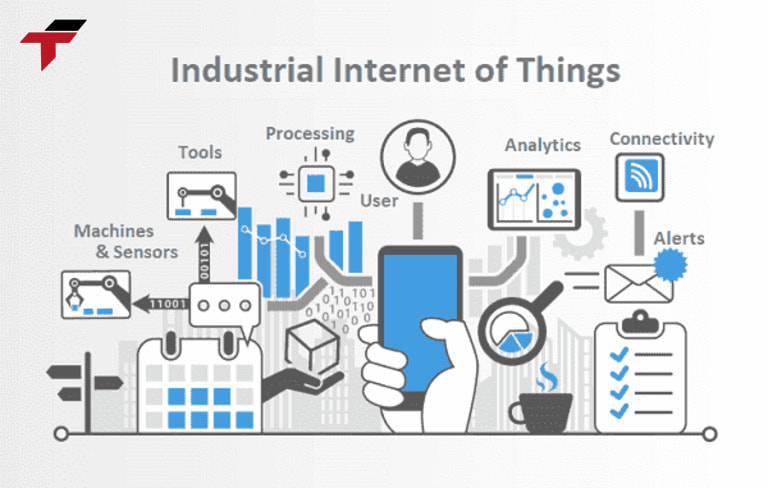
Industrial Internet of Things -IIoT
Variable Frequency Drive – VFD
A VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) is a device that controls the speed of an electric motor by adjusting the frequency of the electrical current supplied to the motor. VFDs save energy and improve motor efficiency in variable speed applications, such as pumps, fans, and compressors.
By using VFDs, plants can reduce energy consumption, extend motor life, and improve overall system efficiency.
Human-Machine Interface – HMI
HMI (Human-Machine Interface) is a tool that helps humans interact with automation systems. This interface provides an intuitive way for operators to monitor and control equipment and machines in the production line.
- Improved Operational Efficiency: Simplifies complex processes and reduces human error.
Enhanced Safety: Provides real-time alerts and control options to prevent accidents. - Better Decision-Making: Visual data enables faster, more informed decisions.
- Remote Monitoring: Modern HMI solutions often allow control from remote locations.
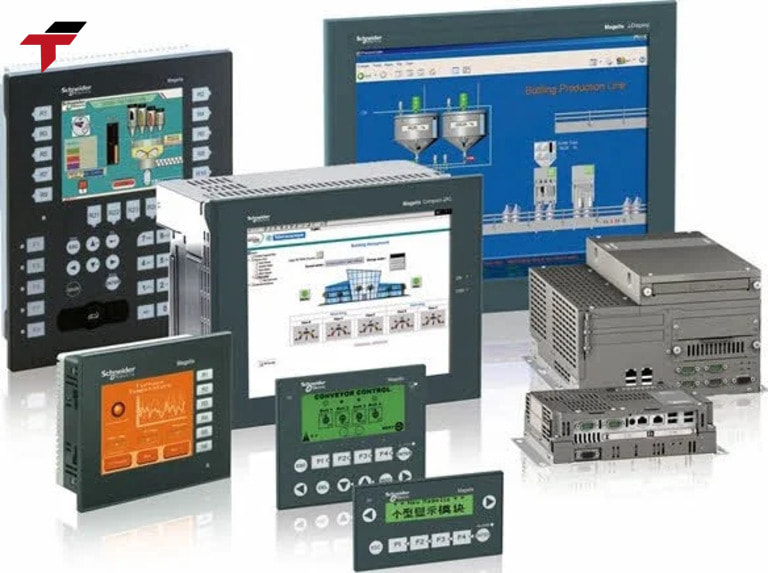

Human-Machine Interface – HMI
Transducer
A transducer is a device that converts signals from one form to another, such as converting temperature to an electrical signal or converting pressure to an electrical signal. Transducers play an important role in measuring and controlling parameters in the manufacturing process.
For example, a temperature transducer can convert the temperature measured from a sensor into an electrical signal that the control system can understand and process.
Conclusion
Understanding key terms in industrial automation is essential for optimizing processes, improving productivity, and staying competitive in the modern industrial landscape. From Automation and PLCs to HMI, IIoT, and transducers, mastering these concepts helps businesses implement efficient, reliable, and intelligent systems.
At Flextech, we provide comprehensive industrial automation solutions, from advanced control systems to smart factory integration, helping companies leverage the latest technologies to enhance performance, reduce costs, and achieve operational excellence. Partnering with Flextech ensures that your business stays at the forefront of Industry 4.0 innovation.


