In industrial environments, a communication protocol is a structured set of rules that allows devices such as Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs), Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), sensors, and supervisory software to exchange information accurately and reliably.
These protocols serve as the digital language that keeps various components of an automation system connected and synchronized. Whether an HMI sends commands to a robotic arm or receives feedback from temperature sensors in a frozen warehouse, communication protocols ensure that all parts of the system “speak” the same language to maintain operational harmony.
What Are the Main Functions of a Communication Protocol?
The core purpose of a communication protocol is to maintain reliable connectivity among all devices in an automation system. However, it also serves several other essential roles:
- Data exchange: Guarantees precise and timely data transfer between machines and software systems.
- Device interoperability: Enables equipment from different manufacturers to function seamlessly on one network.
- Data security: Prevents unauthorized access and manipulation of transmitted information.
- Operational efficiency: Minimizes lag, communication failures, and data loss in warehouse and production processes.
With these functions in place, communication protocols ensure that every signal, command, and feedback loop operates smoothly enhancing reliability across the entire system.

What Are the Main Functions of a Communication Protocol?
How Does Ethernet Support Industrial HMI Communication?
Ethernet is among the most widely adopted communication protocols in automation. It uses a wired local area network (LAN) to connect multiple devices and exchange data in real-time.
Industrial Ethernet variants like Profinet, EtherCAT, and Modbus TCP/IP are now standard in many factories due to their reliability and scalability.
Advantages of Ethernet
- High-speed data transfer: Ideal for real-time process control.
- Easy scalability: Expanding or modifying the system is simple with switches or routers.
Broad compatibility: Works with most industrial controllers and HMI panels.
Remote accessibility: Enables off-site monitoring and troubleshooting.
Disadvantages of Ethernet
- Complex cabling setup: Requires structured planning and installation.
- Electromagnetic vulnerability: May face signal interference in certain environments.
- Security exposure: Needs strong segmentation and protection against cyber threats.
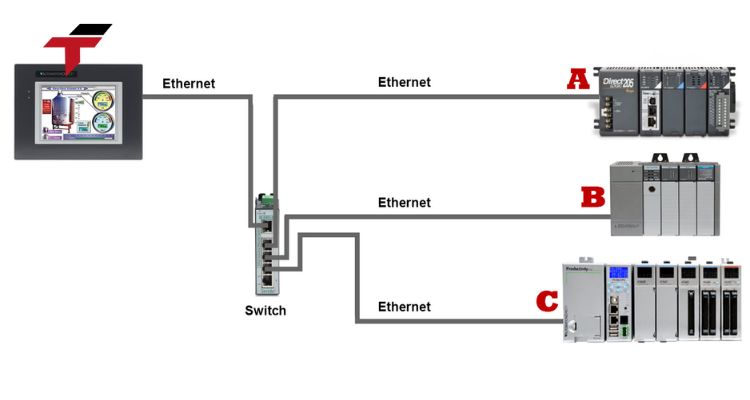
How Does Ethernet Support Industrial HMI Communication?
Why Is SMTP Useful in HMI Applications?
While SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) is primarily known for email transmission, it also serves valuable functions in industrial automation. Many HMI systems use SMTP to send automated email alerts when alarms, system faults, or maintenance reminders occur.
Advantages of SMTP
- Instant notifications: Helps operators respond to issues in real time.
- Remote accessibility: Allows monitoring through emails from any location.
- Simple setup: Supported by most HMI software without extra tools.
Disadvantages of SMTP
- One-way communication: Designed for sending, not receiving or interactive communication.
- Internet dependency: Requires a stable network connection.
- Security risks: Needs SSL/TLS encryption to prevent email interception.
How Does SSH Enhance Remote Management in HMI Systems?
Secure Shell (SSH) is a protocol built for secure remote device access over untrusted networks. In industrial automation, SSH is commonly used for configuring or troubleshooting Linux-based HMI panels, edge computing devices, and industrial gateways.
Advantages of SSH
- End-to-end encryption: Keeps credentials and transmitted data secure.
Strong authentication: Only verified users gain system access. - Remote administration: Enables maintenance without physical presence.
- Automation capability: Allows engineers to run scripts for diagnostics and backups.
Disadvantages of SSH
- Technical complexity: Requires knowledge of command-line operations.
- Password vulnerability: Weak passwords can become security loopholes.
- Lack of visual interface: May challenge users unfamiliar with terminal-based management.
What Should Be Considered When Applying Communication Protocols?
To ensure stable and long-term performance in automated production systems, engineers and operators should take the following points into account:
- Compatibility: Confirm that all connected devices, like HMIs, PLCs, sensors, and SCADA systems, support the same protocol standards.
- Network security: Use encrypted and authenticated communication methods (e.g., SSH, SSL, HTTPS) to protect against unauthorized access.
- Bandwidth management: Allocate sufficient network capacity to avoid delays, particularly in fast-moving systems like conveyor or robotic lines.
- System redundancy: Implement backup communication routes to maintain operation continuity during network failures.
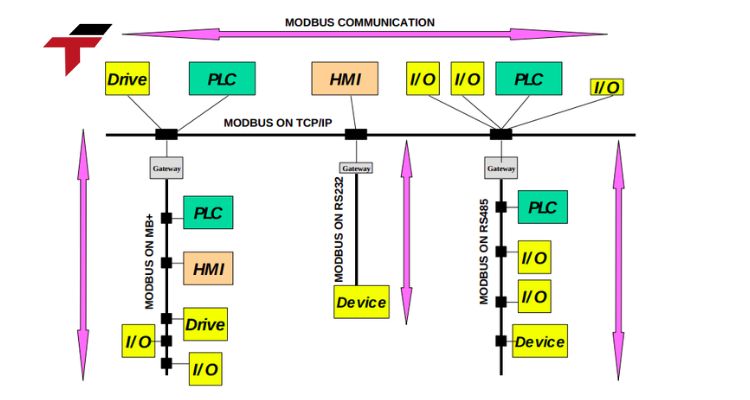
What Should Be Considered When Applying Communication Protocols?
Why Do Communication Protocols Matter in Modern Automation?
Communication protocols form the foundation of industrial connectivity – ensuring that HMIs, PLCs, and sensors operate as one cohesive system.
Selecting the right protocol (or combination of protocols) depends on the specific operational needs, network structure, and cybersecurity requirements of each facility.
As manufacturing shifts toward smarter, interconnected systems, understanding communication protocols is no longer a technical detail—it’s a critical skill for achieving efficiency, reliability, and scalability in Industry 4.0 environments.


