DF-1 Protocol is a proven serial communication standard widely used in industrial automation for PLC-to-PLC and PLC-to-device communication. Known for its reliability, simplicity, and deterministic performance, DF-1 remains crucial in legacy systems and small-to-medium networks. With Flextech, businesses can maintain, upgrade, and integrate DF-1 networks into modern SCADA, HMI, and IoT platforms, ensuring efficient and continuous industrial operations.
What Is the DF-1 Protocol?
DF-1 Protocol is a serial communication protocol developed by Allen-Bradley (Rockwell Automation) for industrial automation applications. It is primarily used for PLC-to-PLC and PLC-to-device communication, providing reliable and deterministic data exchange in manufacturing and industrial processes.
- Definition and Concept: DF-1 allows structured data transmission over serial links (RS-232 or RS-485) using a command-response format with checksums for error detection.
- Origin and Development: Developed in the 1980s by Allen-Bradley, DF-1 became a standard protocol for serial PLC communication, addressing the limitations of early industrial communication systems.
- Importance in Industrial Automation: DF-1 is robust and reliable, widely used in legacy PLC systems, and compatible with SCADA, HMI, and modern automation solutions.
How Does the DF-1 Protocol Work?
DF-1 operates over serial links, enabling structured communication between devices.
- Serial Communication Basics: RS-232 is typically used for short-distance single connections, while RS-485 supports multi-drop networks over longer distances.
- Message Structure: Each DF-1 message contains a command, data payload, and checksum to ensure accurate and reliable communication.
- Half-Duplex vs Full-Duplex: Half-duplex allows one-way communication at a time, while full-duplex supports simultaneous two-way communication.
- Device Addressing and Node Identification: Each device has a unique node address, preventing data conflicts and ensuring commands reach the correct device.
- Error Detection and Retransmission: Checksum validation ensures data integrity, and failed messages are retransmitted automatically.
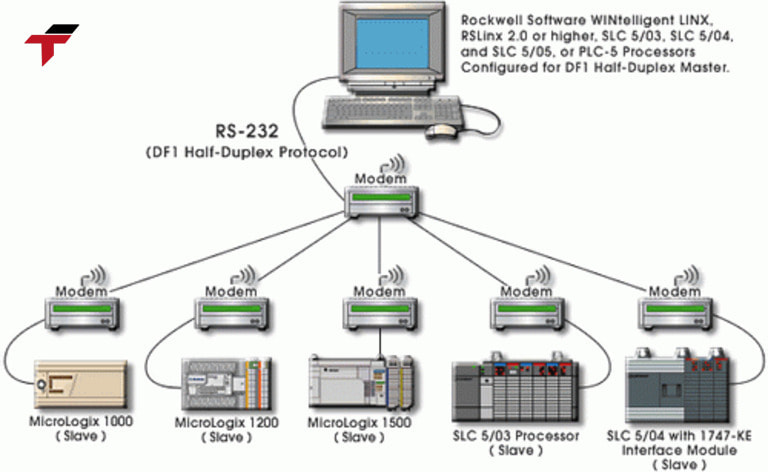
DF-1 operates over serial links, enabling structured communication between devices.
What Are the Advantages of Using DF-1 Protocol?
DF-1 Protocol offers a range of practical benefits that make it a reliable choice for industrial automation, especially in plants using Allen-Bradley PLCs:
- Robust and Proven: DF-1 has been deployed in industrial environments for decades, handling harsh conditions such as electromagnetic interference, temperature fluctuations, and mechanical vibrations. Its proven track record ensures consistent and dependable communication, critical for continuous production lines.
- Easy Implementation: Because DF-1 is natively supported on Allen-Bradley PLCs, engineers can set up communication networks quickly without extensive programming. Configuring ports, setting device addresses, and establishing communication links is straightforward, which reduces setup time and potential errors.
- Legacy System Maintenance: Many factories still operate older PLC models that rely on DF-1. By using this protocol, companies can maintain long-term operations without replacing entire systems, ensuring business continuity and reducing capital expenditure.
- Low Hardware and Software Overhead: DF-1 does not require high-end hardware or complex software stacks. It operates efficiently with minimal memory and processing power, making it ideal for older PLCs and simple devices while maintaining reliability.
- Predictable Timing for Critical Operations: DF-1 is a deterministic protocol, meaning data is transmitted at predictable intervals. This is crucial in time-sensitive industrial applications, such as synchronized conveyor belts, robotic arms, or safety interlocks, where even minor delays could impact operations.
Overall, DF-1 balances simplicity, reliability, and cost-effectiveness, making it suitable for both new and legacy industrial automation networks.
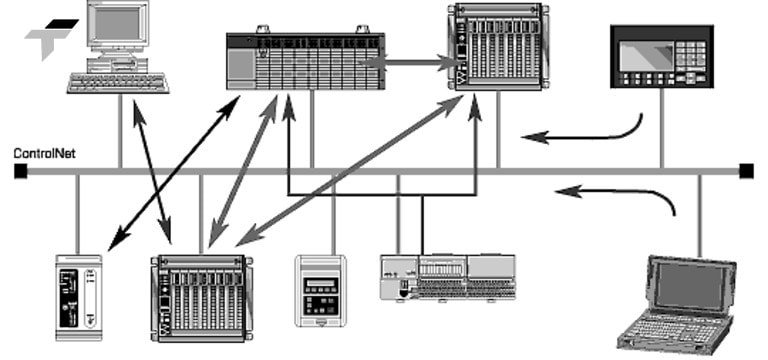
Advantages of Using DF-1 Protocol
What Are the Limitations and Considerations of DF-1 Protocol?
Despite its advantages, DF-1 has certain constraints that engineers and managers need to consider when designing or maintaining automation systems:
- Limited Data Speed: As a serial protocol, DF-1 has lower data throughput compared to modern Ethernet-based solutions. High-volume or real-time applications requiring fast, continuous data transfer may not perform optimally with DF-1.
- Network Size Restrictions: DF-1 is best suited for small to medium networks. Large-scale implementations can encounter signal degradation, timing conflicts, and increased complexity when many nodes are connected. Careful planning of network topology and device addressing is necessary.
- Serial Cabling Requirements: DF-1 relies on RS-232 or RS-485 serial cabling, which can be less flexible than Ethernet in terms of installation, expansion, and troubleshooting. Longer cable runs or complex plant layouts may require repeaters or converters.
- Compatibility Challenges with Modern Systems: Integrating DF-1 networks with modern PLCs, SCADA systems, IoT platforms, or Ethernet-based protocols can be challenging. Protocol converters, gateways, or hybrid network designs may be needed to ensure seamless communication.
- Maintenance Considerations: Legacy DF-1 networks require regular inspection and maintenance, including checking wiring integrity, device addresses, and signal quality. Neglecting these can lead to communication errors, downtime, or equipment failures.
In short, while DF-1 is reliable and cost-effective, it is less suited for high-speed, large-scale, or fully modernized industrial networks, and proper planning is required to maximize its performance.
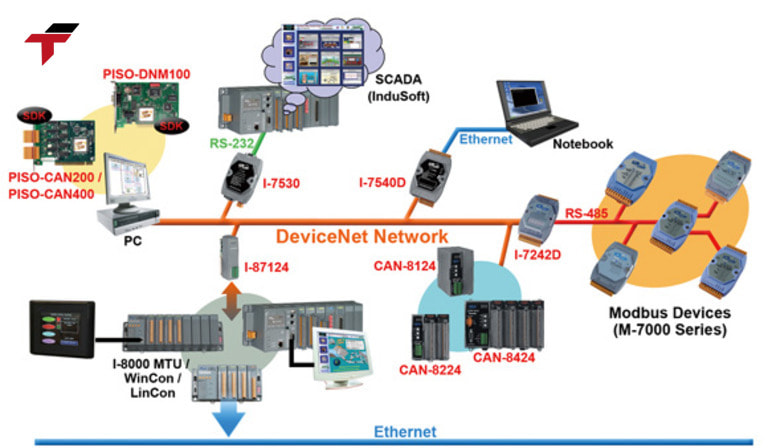
Limitations and Considerations of DF-1 Protocol
What Are the Applications of DF-1 Protocol?
DF-1 Protocol remains widely used in industrial automation due to its simplicity, reliability, and compatibility with legacy Allen-Bradley PLCs. Key applications include:
- PLC-to-PLC Communication in Manufacturing Lines: DF-1 allows direct communication between multiple PLCs, enabling synchronized control of production lines, assembly machines, and robotic cells. This ensures coordinated operations and real-time data exchange across devices.
- Industrial Process Monitoring and Control: DF-1 networks are often used to monitor sensors, actuators, and other field devices, providing accurate feedback to control systems. This supports process automation, safety interlocks, and operational efficiency.
- Integration with SCADA and HMI Systems: DF-1 facilitates seamless communication with SCADA platforms and HMI panels, allowing operators to visualize, monitor, and control industrial processes in real time.
- Remote Device Communication over Serial Links: DF-1 can connect devices over RS-232 or RS-485 serial links, enabling communication with remote equipment, distributed sensors, or field instruments in factories and process plants.
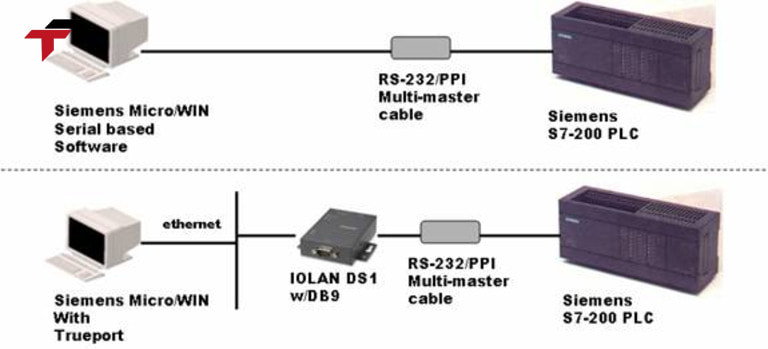
DF-1 Protocol remains widely used in industrial automation due to its simplicity, reliability, and compatibility with legacy Allen-Bradley PLCs
What Is the Relevance of DF-1 Protocol Today and How Can Flextech Help?
Despite the rise of Ethernet-based protocols, DF-1 continues to play a vital role in legacy industrial networks. It provides robust, deterministic communication, allowing companies to maintain operational continuity without large-scale investments in new systems.
Flextech’s Role:
- Supporting Existing DF-1 Systems: Flextech provides technical support, maintenance, and troubleshooting for DF-1 networks to ensure stable and reliable operations.
- Integration and Modernization: Flextech offers integration solutions with SCADA, HMI, and IoT platforms, allowing DF-1 networks to interface with modern automation infrastructure.
- System Upgrades and Retrofits: Flextech assists companies in upgrading legacy PLC networks while retaining DF-1 communication, extending the life of existing industrial assets.
- Consulting and Training: Flextech also provides expert consulting and operator training, helping teams optimize DF-1 network performance and ensure proper handling of legacy systems.
In summary, DF-1 remains a trusted industrial protocol for legacy systems, and Flextech helps businesses maximize its efficiency, integrate with modern technologies, and ensure long-term operational reliability.


