The DirectNET protocol is a serial communication standard developed for DirectLOGIC PLCs, providing simple, reliable, and cost-effective connectivity for industrial automation systems. Designed primarily for small to medium networks, DirectNET allows master devices, such as PCs, HMIs, or SCADA systems, to communicate seamlessly with multiple slave PLCs. Understanding how DirectNET works, its key features, and its applications can help manufacturers maintain legacy systems, extend network capabilities, and optimize industrial processes efficiently.
What Is DirectNET Protocol?
The DirectNET protocol is a serial communication protocol developed for DirectLOGIC PLCs, enabling reliable data exchange between controllers, operator interfaces, and supervisory systems. Designed primarily for small to medium-scale automation networks, DirectNET provides a simple, stable, and cost-effective method for connecting multiple PLCs and devices using traditional serial communication standards such as RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485.
DirectNET operates on a command–response model, where a master device—typically a PC, HMI, SCADA system, or a primary PLC—communicates with one or more slave PLCs. Each device in the network is assigned a unique address, allowing the master to send instructions directly, request data, monitor device status, or modify control parameters.
How Does DirectNET Work?
Understanding how the DirectNET protocol works is essential for setting up reliable communication between DirectLOGIC PLCs and other devices in an automation network. While the protocol can involve multiple technical details, its operation can be summarized clearly in five main steps.
- Network Setup and Addressing: Connect PLCs and devices using RS-232, RS-422, or RS-485, and assign a unique address to each slave device.
- Communication Configuration: Set common parameters such as baud rate, parity, data bits, and stop bits for all devices to ensure proper serial communication.
- Master Sends Commands: The master device (PC, HMI, or primary PLC) sends a request to a specific slave, instructing it to read, write, or execute control actions.
- Slave Processes and Responds: The addressed slave validates the request, performs the action, and sends back data or an acknowledgement to the master.
- Polling and Error Handling: The master continues polling devices in sequence, monitoring responses and retrying in case of timeouts, errors, or communication failures.
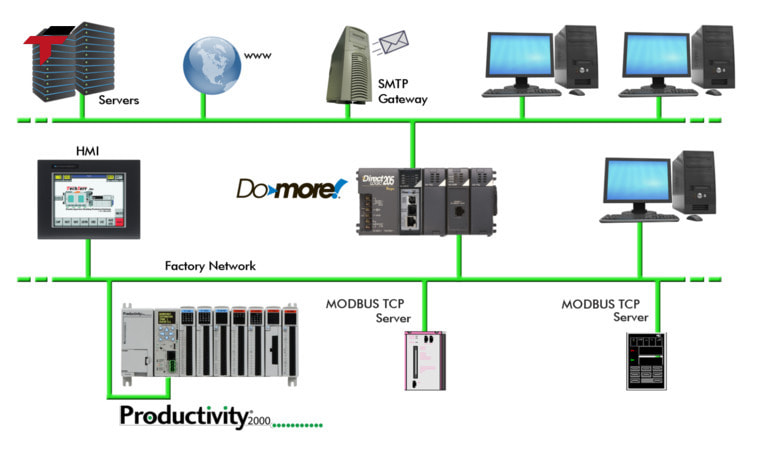
DirectNET can be summarized clearly in five main steps.
What Are the Key Features of the DirectNET Protocol?
DirectNET is a straightforward and reliable serial communication protocol with several key features that make it suitable for industrial automation:
- Supported Baud Rates and Communication Settings: DirectNET supports a range of standard serial communication speeds, typically from 1,200 bps up to 19,200 bps. It allows configuration of parity, data bits, and stop bits to match the requirements of the network and ensure accurate data transmission.
- Device Addressing and Node Structure: Each device in a DirectNET network is assigned a unique address, allowing the master to communicate with individual slaves efficiently. The protocol follows a master–slave architecture, ensuring orderly communication without collisions.
- Types of Commands Supported: DirectNET allows a variety of commands, including reading and writing to memory locations, controlling outputs, monitoring device status, and executing special instructions. This versatility enables it to handle essential control and monitoring tasks in an automation system.
- Compatibility with DirectLOGIC PLCs: The protocol is fully compatible with multiple families of DirectLOGIC PLCs (such as DL05, DL06, DL205, DL305, and DL405), providing seamless communication between controllers, HMIs, and SCADA systems.
What Components Are Required for DirectNET Communication?
To set up a functioning DirectNET network, several hardware and software components are required:
- PLCs Supporting DirectNET: DirectLOGIC PLCs such as DL05, DL06, DL205, DL305, and DL405 are commonly used as slave devices in a DirectNET network.
- Communication Interfaces: Depending on network size and distance, devices can connect via RS-232 (point-to-point), RS-422, or RS-485 (multi-drop) serial interfaces.
- Cables, Adapters, and Converters: Proper serial cables are needed to connect devices, with adapters or converters required for interfacing between different serial standards or for extending network distance.
- PC or HMI/SCADA for Master Control: A master device, typically a PC with control software, HMI, or SCADA system, manages communication by sending commands to slave PLCs, polling their status, and processing responses.
To set up a functioning DirectNET network, several hardware and software components are required
What Are the Advantages of the DirectNET Protocol?
DirectNET offers several benefits that make it a reliable choice for industrial automation, especially in legacy systems:
- Simple and Reliable Communication for Small Networks: The protocol is easy to configure and maintain, providing stable serial communication between PLCs and devices.
- Ideal for Legacy System Maintenance and Extensions: DirectNET works seamlessly with older DirectLOGIC PLCs, making it perfect for extending or upgrading existing automation networks without replacing all hardware.
- Low Hardware Requirements: Minimal additional hardware is needed—standard serial interfaces and simple cabling are sufficient for most small to medium setups.
- Cost-Effective for Basic Automation Tasks: DirectNET provides dependable communication at a lower cost compared to modern, more complex protocols, making it ideal for small-scale automation projects.
What Are the Challenges and Limitations of the DirectNET Protocol?
While DirectNET is effective for certain applications, it has limitations that manufacturers should consider:
- Limited Speed Compared to Modern Ethernet-Based Protocols: Serial communication restricts data transfer rates, making it less suitable for high-speed or data-intensive applications.
- Not Ideal for Large Networks or High Data Loads: As network size and traffic increase, polling delays and communication bottlenecks may occur.
- Compatibility Issues with Newer Automation Platforms: DirectNET may not integrate easily with modern PLCs, Ethernet-based systems, or IIoT networks without additional converters or gateways.
- Need for Serial Communication Knowledge: Engineers and operators must understand serial network configuration, addressing, and troubleshooting to ensure reliable operation.
While DirectNET is effective for certain applications, it has limitations that manufacturers should consider
Conclusion
The DirectNET protocol remains a reliable and cost-effective solution for connecting DirectLOGIC PLCs and other industrial devices, particularly in legacy automation systems. Its simplicity, low hardware requirements, and stability make it ideal for small networks, machine-to-machine communication, and extending existing control systems.
While it has limitations in speed and scalability compared to modern Ethernet-based protocols, DirectNET continues to serve a vital role in many industrial applications.
At Flextech, we specialize in providing comprehensive automation solutions, including DirectNET integration, configuration, and troubleshooting. Our team helps factories optimize legacy systems, ensure reliable communication between PLCs and devices, and seamlessly bridge older networks with modern automation platforms. With Flextech, manufacturers can maintain high performance, efficiency, and future-proof their industrial automation systems.


