The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is revolutionizing the industrial sector by connecting smart devices, sensors, and machines to optimize processes, enhance efficiency, and reduce costs. Acting as a bridge between traditional industrial operations and modern digital technology, IIoT is a key component of Industry 4.0. In this guide, we explore what IIoT is, its advantages, challenges, and real-world applications across industries, showing why it’s essential for digital transformation.
What is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT)
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is the application of Internet of Things (IoT) technology to the industrial sector. It uses smart devices such as sensors, machines, radio frequency identification tags and control systems to improve manufacturing processes. These devices are connected via the Internet to collect data, exchange and analyze data.
The IIoT network enables M2M communication and data transmission between the central system and all IIoT-integrated devices. This technology is considered a key component of the transition to the Industry 4.0 era and has the potential to revolutionize many other industries.
What benefits does the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) bring to business?
Not only does it help optimize operating processes, IIoT also creates breakthroughs in increasing productivity, improving product quality and reducing production costs. Let’s explore the outstanding benefits that IIoT brings, helping businesses not only compete but also lead in the era of Industry 4.0.
- Increase productivity: Thanks to automation and data analysis, IIoT helps businesses optimize production processes, thereby increasing labor productivity without increasing the number of employees.
- Improve product quality: Data from sensors helps detect errors in the production process immediately, ensuring high-quality products before reaching customers.
- Predict maintenance time in advance: Businesses use real-time data from IIoT systems to predict when to repair and maintain machinery. Thereby ensuring that the production line is periodically checked, helping to operate more efficiently.
- Asset management: Manufacturers, suppliers and customers can use the IIoT network system to track the location, status and condition of products throughout the production process. When there is damage, the system will send timely warnings to relevant parties to handle the problem as quickly as possible.
- Meet customer needs: When connected to the IIoT network, manufacturers can collect and analyze customer insights. From there, businesses can design products that best suit customer needs.
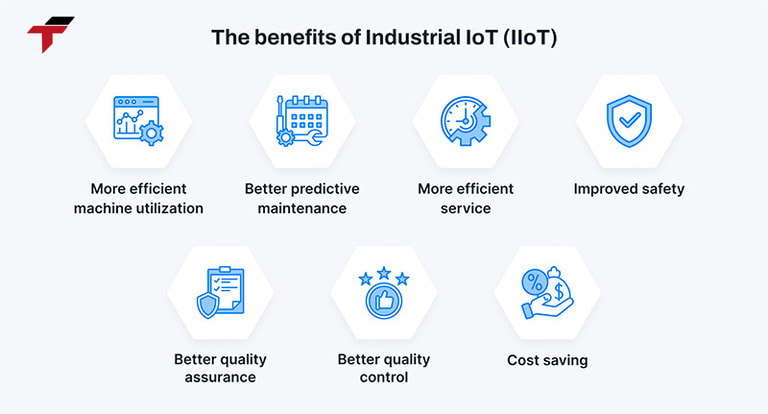
Benefits of the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) bring to business
What challenges does the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) face?
Although the Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) brings many outstanding benefits to industries, the implementation of this technology also comes with many major risks and challenges. Here are common issues that businesses need to consider when applying IIoT:
- Cybersecurity Risks: IIoT networks connect thousands of devices, sensors, and systems on different platforms, creating many vulnerable points of attack.
- Difficult to integrate with legacy systems: Many factories still use traditional industrial equipment (Legacy Systems), and integrating these systems with IIoT requires a large investment in both time and technology.
- High initial costs: Significant investments in equipment, network infrastructure, and data analysis software are required, which can be difficult for small and medium-sized businesses.
- Human resource training: IIoT requires personnel with knowledge of digital technology, data analysis, and smart system operations. This is a big challenge for businesses that are unfamiliar with new technology.

Here are common issues that businesses need to consider when applying IIoT
In which industries is Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) applied?
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is being widely applied in many industries, from manufacturing, energy to logistics and agriculture. Here are some typical industries:
- Agriculture: IIoT helps collect data about the environment, soil, weather and crop conditions through sensors. Data analysis systems then allow automatic adjustment of appropriate water, fertilizer and lighting.
- Manufacturing: Real-time data analysis systems enable detection of problems such as technical faults or overloading, thereby improving operational efficiency and predictive maintenance.
- Automotive industry: Data from sensors is collected to monitor vehicle health and provide information on driving behavior.
- Logistics and transportation: IIoT helps track the location, condition and status of goods during transportation. Trucks, ships and planes can be equipped with sensors to collect data on fuel consumption, engine performance and travel routes.
- Healthcare: Smart medical devices in hospitals are connected to monitor patient conditions or machine performance.
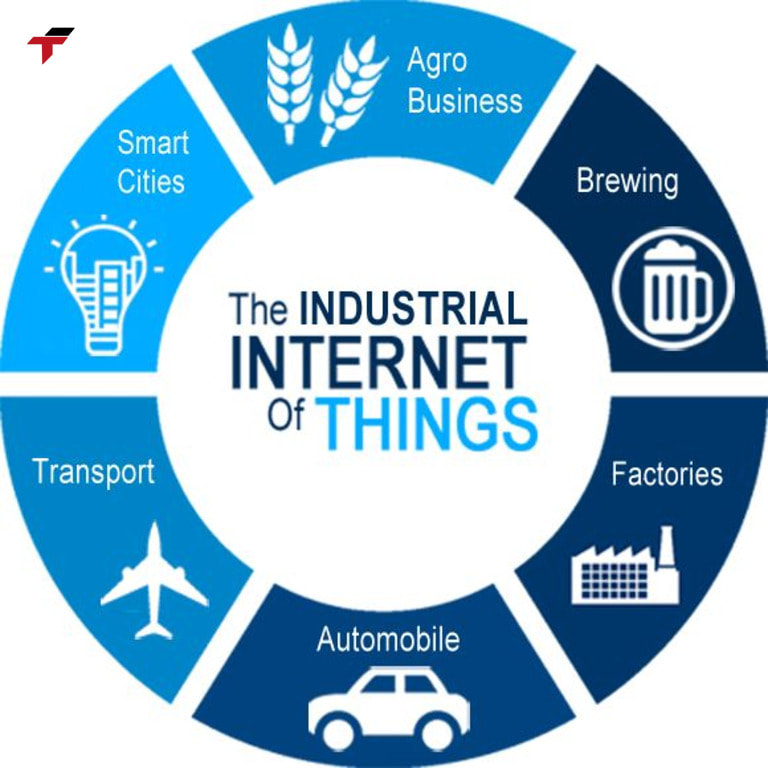
Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is being widely applied in many industries
What is the difference between IOT and IIOT?
IoT connects everyday devices to improve convenience and efficiency, while IIoT focuses on industrial environments to optimize operations, enhance safety, and reduce costs. Understanding the difference helps businesses apply the right technology for their needs.
| IIoT | IoT | |
| Objectives | IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) is a network of connected devices and sensors in industrial environments to optimize performance, increase safety, and reduce operating costs. | IoT (Internet of Things) is a network of smart devices in everyday life to enhance convenience, efficiency, and user experience. |
| Application scope | Used in heavy industries such as manufacturing, energy, oil and gas, logistics, and mining. | Mainly applied in areas such as smart homes, wearables, remote healthcare systems, and smart cities. |
| Connection technology | Use more powerful connection technology such as industrial Ethernet, 5G technology, and secure protocols such as OPC-UA, Modbus. | Use connection technology such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, and Zigbee, suitable for small ranges. |
| Complexity | Need to integrate multiple devices, systems, and technologies in an industrial environment. | Devices often operate independently or have limited interaction. |
| Scalability | Scalable into large networks with thousands of sensors. | Poor scalability because it is only for personal use |
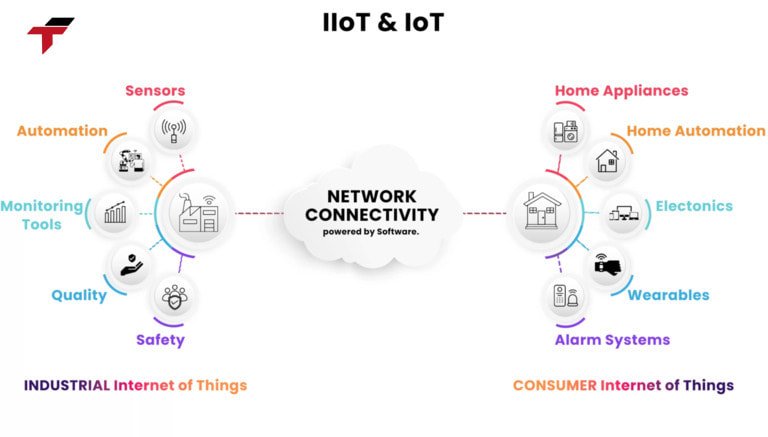
Difference between IOT and IIOT
How Does IIoT Integrate with Other Industry 4.0 Technologies?
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) doesn’t operate in isolation—it works hand-in-hand with other Industry 4.0 technologies to create fully connected, intelligent, and efficient industrial systems. By integrating IIoT with advanced technologies, businesses can achieve higher automation, better decision-making, and enhanced productivity.
- Integration with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML): IIoT devices generate vast amounts of data from sensors, machines, and industrial equipment. AI and ML analyze this data to identify patterns, predict equipment failures, optimize processes, and support real-time decision-making.
- Connection with Big Data and Analytics: IIoT systems collect high-volume, high-velocity data, which can be processed using big data analytics tools. Insights derived from this analysis help businesses optimize production schedules, reduce waste, and improve product quality, enabling smarter, data-driven strategies.
- Collaboration with Cloud Computing: Data collected from IIoT devices is often stored and processed in the cloud, enabling remote monitoring, centralized control, and scalable computing power.
- Interaction with Robotics and Automation Systems: IIoT networks provide real-time information to industrial robots and automated systems, enhancing precision, efficiency, and flexibility.
- Connection with Augmented Reality (AR) and Digital Twins: IIoT feeds real-time data into AR applications and digital twin models, allowing operators to visualize equipment performance, simulate production scenarios, and perform virtual troubleshooting.
FAQ: Common Questions About IIoT
1. How does IIoT differ from traditional industrial automation?
Traditional automation focuses on controlling machines and predefined processes, often operating in isolated systems.
IIoT, on the other hand, connects machines, sensors, and software through the internet to enable real-time data collection, analysis, and optimization. This makes industrial operations smarter, more flexible, and data-driven.
2. Can IIoT be applied in small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs)?
Yes. Modern IIoT solutions are increasingly scalable and cost-effective, allowing SMEs to adopt them without large investments. Businesses can start small—such as with sensor-based monitoring—and gradually expand as their needs grow.
3. What types of data do IIoT devices typically collect?
IIoT devices gather operational data such as temperature, pressure, vibration, energy usage, equipment health, production output, and environmental conditions. This data helps businesses improve performance, prevent downtime, and optimize decision-making.
4. How does IIoT contribute to predictive maintenance?
IIoT sensors continuously track machine conditions and detect early signs of malfunction. This data allows systems to predict when maintenance is needed, reducing unexpected downtime, extending equipment lifespan, and lowering repair costs.
Conclusion
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is more than just a technological trend—it’s a transformative force that is reshaping the way industries operate. By connecting machines, sensors, and data systems, IIoT enables businesses to achieve higher productivity, reduce downtime, improve product quality, and optimize resources.
Although challenges such as cybersecurity, integration complexity, and initial investment remain, the long-term benefits make IIoT an essential component of any modern digital transformation strategy.
For businesses seeking a reliable partner to implement IIoT solutions, Flextech offers the expertise you need. With strong capabilities in automation, digital transformation, and industrial connectivity, Flextech helps organizations design tailored IIoT systems, integrate them seamlessly with existing infrastructure, and ensure secure, scalable long-term operation.


