Human-Machine Interfaces (HMIs) serve as the bridge between operators and industrial machines, enabling efficient monitoring and control. However, for an HMI to function effectively, it must rely on robust communication protocols that allow it to exchange data seamlessly with PLCs, sensors, and other automation devices.
These standardized communication systems, known as HMI protocols, define how data is transferred between devices. Among the most widely used are Modbus, Profibus, and OPC UA, each offering distinct features, architectures, and advantages. Let’s explore how they work and which one might best suit your automation requirements.
What Is the Modbus Protocol and How Does It Work?
Modbus, introduced by Modicon in 1979, is one of the earliest and most popular industrial communication protocols. Designed to facilitate communication between controllers, sensors, and other field devices, Modbus remains a preferred choice for its simplicity and reliability.
Key Benefits of Modbus
- Ease of implementation: Simple setup and widely supported across automation devices.
- Open and non-proprietary: Free to use, making it accessible for various industries.
- Flexible connectivity: Supports both serial communication (Modbus RTU, Modbus ASCII) and Ethernet-based communication (Modbus TCP/IP).
- Broad compatibility: Works seamlessly with most PLCs, HMIs, SCADA systems, and industrial instruments.
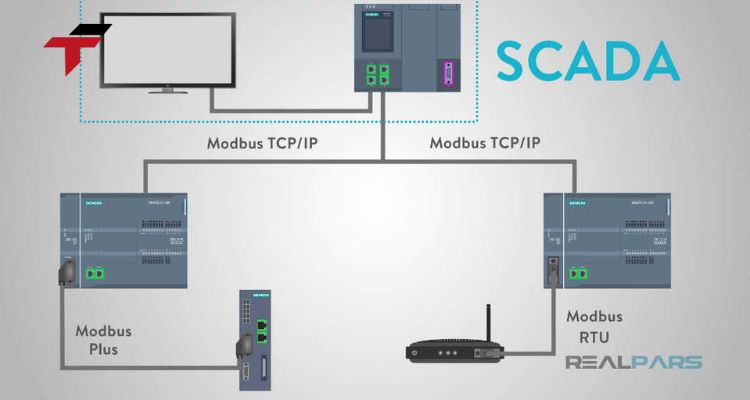
How Modbus Operates
Modbus uses a master-slave communication structure. The master device (often the HMI or controller) sends requests, and slave devices respond with data or acknowledgments. In Modbus TCP/IP, communication occurs via Ethernet, improving speed and allowing longer-distance data transmission compared to serial connections.
Limitations of Modbus
- No built-in security: Lacks encryption or authentication mechanisms.
- Simplistic data handling: Uses basic data formats that limit complex data structures.
- Single-master constraint: Traditional Modbus networks can only operate with one master device.
What Is the Modbus Protocol and How Does It Work?
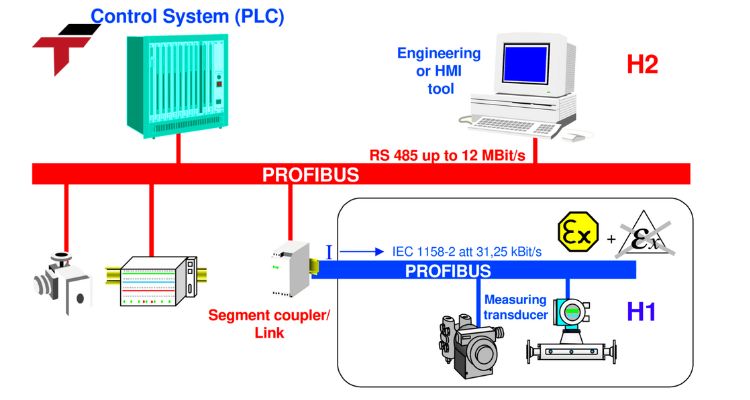
Why Choose Profibus for Your Automation System?
Profibus (Process Field Bus), developed by Siemens, is another highly reliable communication protocol used in factory and process automation. Known for its robust performance and real-time communication, Profibus remains popular in industrial environments worldwide.
Advantages of Profibus
- High-speed data transfer: Supports up to 12 Mbps in Profibus DP mode.
- Deterministic communication: Ensures precise timing, ideal for real-time applications.
- Advanced diagnostics: Allows detailed monitoring and troubleshooting of network issues.
- Vendor interoperability: Supported by multiple manufacturers under PROFIBUS & PROFINET International (PI) standards.
How Profibus Works
Profibus operates on master-slave or token-passing principles and comes in two major variants:
- Profibus DP (Decentralized Peripherals): Optimized for high-speed communication with sensors and actuators.
- Profibus PA (Process Automation): Designed for hazardous or process-oriented environments.
A Profibus master manages cyclic and acyclic communication, ensuring efficient data exchange and diagnostic feedback. It supports up to 126 devices on a single network.
Drawbacks of Profibus:
- Complex setup: Installation requires specific cables, connectors, and configuration tools.
Less flexible: Not as adaptable as Ethernet-based systems. - Gradual phase-out: Being replaced by more modern technologies like Profinet and OPC UA.
Why Choose Profibus for Your Automation System?
What Makes OPC UA the Future of Industrial Communication?
OPC UA (Open Platform Communications Unified Architecture) represents the evolution of industrial communication standards. Developed by the OPC Foundation, it extends beyond traditional protocols by integrating advanced data modeling, security, and cloud compatibility.
Key Advantages of OPC UA
- Cross-platform compatibility: Operates on Windows, Linux, and embedded devices.
- Enhanced security: Built-in encryption, authentication, and access control.
- Comprehensive data modeling: Handles complex hierarchical data structures.
- Scalable architecture: Suitable for both small devices and enterprise-level systems.
- IIoT and cloud integration: Perfect for smart factories and Industry 4.0 applications.
How OPC UA Works
Using a client-server architecture, OPC UA enables secure, structured communication between devices. The server (PLC or controller) publishes data, while the client (HMI or SCADA system) reads, subscribes to, or logs this data in real time.
OPC UA supports multiple communication channels:
- Binary TCP: Optimized for local, high-performance networks.
- HTTP/HTTPS: Enables secure, firewall-friendly communication over the web.
- MQTT: Ideal for IoT and cloud-based applications.
Challenges of OPC UA
- Complexity: Implementation requires specialized knowledge and setup.
- High resource demand: Consumes more processing power and memory.
- Network reliance: Performance depends heavily on network stability and configuration.
What Makes OPC UA the Future of Industrial Communication?
Which HMI Protocol Is Right for Your Application?
Choosing the right protocol depends on your system requirements, infrastructure, and future scalability goals:
| Protocol | Best For | Key Strengths | Limitations |
| Modbus | Legacy or small-scale systems | Simple, low-cost, widely supported | No security, limited data structure |
| Profibus | Real-time factory automation | High speed, reliable, deterministic | Complex setup, being phased out |
| OPC UA | Smart factories, IIoT systems | Secure, scalable, cloud-ready | Requires more resources and expertise |
Conclusion
While Modbus and Profibus continue to play essential roles in legacy and mid-tier systems, OPC UA has emerged as the leading protocol for modern industrial automation. It supports secure, scalable, and interoperable communication—key factors in the transition toward Industry 4.0 and digital transformation.
Before selecting an HMI protocol, evaluate your operational goals, device ecosystem, and long-term technology roadmap. Choosing the right communication foundation today ensures efficiency, compatibility, and growth for tomorrow’s connected factory.


