A Programmable Logic Controller (PLC) is a robust industrial computer designed to control machines and processes within manufacturing environments. Engineered to endure harsh industrial conditions such as vibration, humidity, and electrical noise, PLCs are the backbone of automated systems, including assembly lines, robotics, and conveyor operations.
On the other hand, a Human Machine Interface (HMI) acts as the bridge between human operators and industrial controllers like PLCs. It provides a visual, interactive platform—through panels, touchscreens, or graphical displays—allowing users to monitor and control processes intuitively.
Integrating these two systems is crucial for efficient, reliable industrial automation. Let’s explore how PLC and HMI communicate, their benefits, and the common challenges that can occur during integration.
How Do You Integrate a PLC with an HMI?
Establishing communication between a PLC and an HMI requires proper hardware setup, protocol selection, and programming to ensure seamless data flow between both systems. Here’s how to achieve effective integration:
1. Choose the Right Communication Protocol
The communication protocol determines how data is exchanged between devices. Popular options include Modbus, Ethernet/IP, Profibus, Profinet, and OPC UA. Choosing a protocol that both your PLC and HMI support ensures compatibility and reliable data transfer.
2. Configure Network Settings and IP Addresses
For Ethernet-based communication, assign static IP addresses to the PLC and HMI. Matching network parameters such as port numbers and baud rates—is critical to maintaining consistent connectivity.
3. Map PLC Tags to HMI Variables
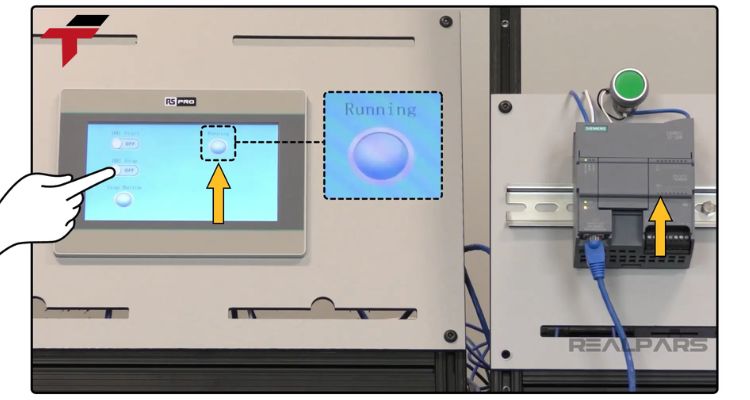
Tags are data points or variables that store real-time values in the PLC. Each tag must be correctly mapped within the HMI software so the display can show accurate data and operators can send control commands back to the PLC.
4. Program Both PLC and HMI
In PLC programming software, define the logic and assign data tags. Meanwhile, in HMI design software, create the graphical interface gauges, buttons, charts and link these elements to the corresponding PLC tags.
5. Test and Troubleshoot the System
Before going live, verify that the communication is functioning correctly. Check if data is transmitted accurately, confirm that the operator can send commands to the PLC, and ensure alarms and event logs display as expected.

How Do You Integrate a PLC with an HMI?
What Are the Benefits of Data Exchange Between PLC and HMI?
Integrating a PLC with an HMI brings multiple operational and strategic advantages:
- Real-Time Process Visualization: Operators can monitor live data such as temperature, pressure, or motor speed directly from the HMI. This real-time visibility supports quicker decision-making and improved system reliability.
- Enhanced Control and Flexibility: Rather than making manual adjustments on machinery, operators can modify parameters directly through the HMI. This feature is especially valuable for remote control or large-scale systems.
- Efficient Alarm and Event Management: Critical system conditions like overloads or malfunctions are immediately shown on the HMI via visual or audible alarms. This allows faster corrective action, minimizing downtime.
- User Access and Security: HMIs allow configuration of user access levels, so only authorized personnel can perform specific operations, such as system resets or parameter modifications. This helps prevent unauthorized actions and maintains safety standards.
- Reduced Human Error: Replacing manual input with automated and graphical interfaces minimizes operator mistakes and ensures greater consistency in process execution.
What Problems Can Occur During PLC and HMI Data Exchange?
While integration provides many benefits, it can also introduce challenges if not properly managed:
- Connection Loss: Loose cables, incorrect IP settings, or hardware issues can interrupt communication between the PLC and HMI, causing data loss or unresponsive screens.
- Tag or Address Mismatch: Incorrect tag mapping between the PLC and HMI can result in blank fields, wrong readings, or malfunctioning controls.
- Protocol Compatibility Issues: Not all PLCs and HMIs support the same communication protocols, especially when sourced from different manufacturers. In these cases, a protocol converter or OPC UA gateway may be necessary.
- Cybersecurity Risks: When the HMI is connected to a broader network, it becomes vulnerable to cyber threats. Implementing firewalls, authentication layers, and encrypted communication (e.g., OPC UA) enhances data protection.
What Problems Can Occur During PLC and HMI Data Exchange?
Conclusion
Integrating PLCs and HMIs is at the heart of modern industrial automation. When done correctly, it ensures real-time control, better decision-making, and enhanced operational safety.
From choosing the right communication protocol and mapping tags accurately to maintaining secure and stable connectivity, every integration step contributes to optimal system performance.
By understanding potential issues such as connectivity errors or protocol mismatches, engineers can ensure smoother operations, minimal downtime, and a more intelligent, responsive industrial environment.


