Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) are the backbone of industrial automation, and choosing the right programming language is key to maximizing efficiency and reliability. In this guide, we explore the five most popular PLC programming languages, their unique features, benefits, and applications, helping engineers and businesses make informed decisions for successful automation projects.
What is Programming Language?
A programming language is a set of rules, syntax, and instructions written by programmers to provide instructions for computers to process and perform tasks. Through programming languages, humans communicate commands and logic for machines to understand and execute.
Computers only understand binary language (strings of 0 and 1 bits), then programming languages allow users to translate strings of 1 and 0 into something that humans can understand and write.
What is the difference between High-level programming languages & Low-level languages?
| High-level language | Low-level language | |
| Level of abstraction | Closer to human language, easy to understand and learn. | Low-level programming languages are closer to machine code or binary code |
| Readability | Easy | Difficult |
| Target of use | For programmers developing software, applications. | For system engineers, embedded programmers or hardware controllers. |
| Speed | Usually slower because it takes time to translate into machine code for computers. | Fast and efficient, directly optimized for hardware. |
| Application | Developing web, mobile, management software applications… | Programming operating systems, embedded, or device controllers. |
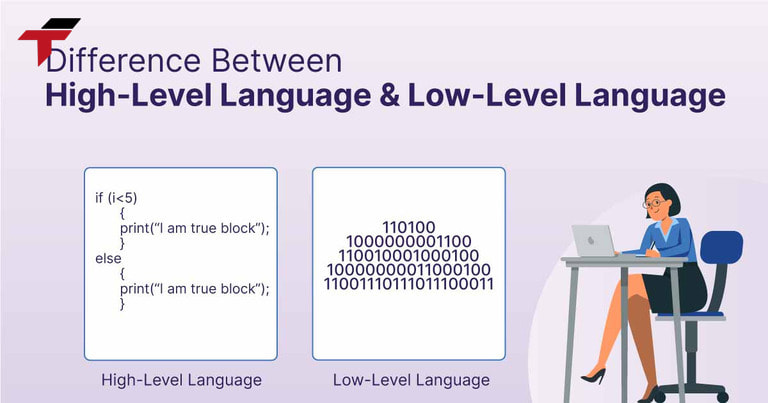
Difference between High-level programming languages & Low-level languages
How many types of programming languages are there? Advantages and disadvantages of each type.
PLC programming languages such as Structured Text (ST), Sequential Function Charts (SFC), Ladder Logic Diagram (LD), Function Block Diagram (FBD), and Instruction List (IL) belong to high-level programming languages in the field of automation control, although their levels of abstraction are different.
Although these languages are specific to PLCs, they are still classified as high-level programming languages because they make it easy for programmers to express control logic without directly manipulating binary code or hardware.
Structured Text (ST)
Text programming has a structure similar to high-level programming languages such as Pascal or C, C++. It is the easiest language to use for programs, using mathematical calculations, formulas, algorithms and programs with large amounts of data.
This language includes decision loops, case statements, IF-Then logic and other features of high-level languages, making it one of the most powerful PLC programming languages available.
Manufacturers supporting ST/STL programming language: Schneider, ABB, B&R, Siemens…
Advantages
- It is very organized and good at computing large mathematical calculations.
- It will enable you to cover some instructions that are not available in some other languages like the Ladder Diagram.
Disadvantages
- The syntax can be difficult.
- It is harder to debug because of its more complex structure. There is no visual queue, less visual aids, and there is often more code on a single line.
- It is difficult to edit online

Text programming has a structure similar to high-level programming languages such as Pascal or C, C++
Sequential Function Charts (SFC)
Sequential Function Charts is the simplest type of PLC programming language, consisting only of decision logic. It can be understood as a graphical means of partitioning code and displaying the status or operating mode visually. However, this language is not always suitable for all applications.
Sequential Function Charts will work from firs block box ( step 1 ) and then if it is done it will go to the next step ( step 2) and then if it is done it will go to next step ( step 3) to reach the final step.
Manufacturers supporting SFC programming language: Mitsubishi, Schneider, Siemens, ABB…
Advantages
- Simplify complex processes by breaking them into more manageable parts.
- Easy to troubleshoot
- Integrate with structured text (ST) programming languages to create advanced logic flows.
Disadvantages
- Limited use cases such as: requiring concurrency, high processing speed, or complex processes.
- Difficult to deploy and troubleshoot: when process paths are split into multiple streams, it becomes difficult to deploy separate flow paths resulting in a robust chain.
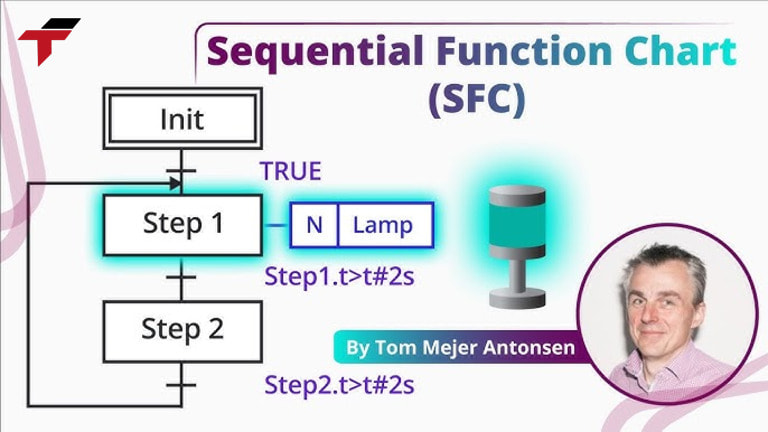
Sequential Function Charts is the simplest type of PLC programming language
Ladder Logic Diagram (LD)
Ladder Logic is the most widely used high-level programming language for PLC programming because it is designed to replace wired relay control systems. It is a graphical programming language that represents logic operations with symbolic notation.
Ladder Logic is designed with a structure like a ladder, consisting of two parallel vertical lines connected by horizontal lines. On these horizontal lines, symbols such as contacts and coils are used to represent input signals (e.g. sensor values) and outputs (e.g. motor control commands). This layout helps simulate relay circuits visually.
Manufacturers supporting LAD programming language: ABB, Siemens, Schneider, Mitsubishi…
Advantages
- The rungs allow it to be organized and easy to follow.
- It supports online editing very successfully.
Disadvantages
- The main disadvantage is that there are some instructions that are not available, which might make it more difficult for programming such as motion or batching
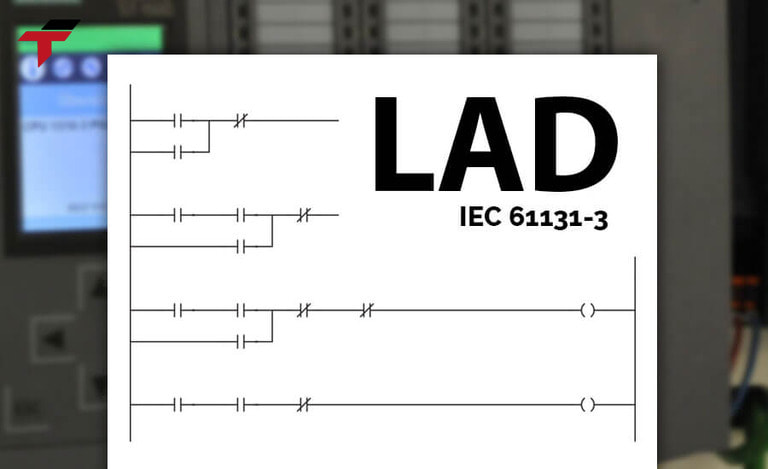
Ladder Logic is the most widely used high-level programming language for PLC programming
Function Block Diagram (FBD)
This is a function block diagram – a widely used programming language that provides a wide range of capabilities and is used to program any function in a PLC program. This is the basic language for all PLC programmers, a great tool for implementing everything from logic to timers, PID controllers or even SCADA systems. The language helps to group multiple lines of programming into one block or several function blocks.
Manufacturers supporting FBD programming language: ABB, Schneider, Siemens, B&R…
Advantages
- User-friendly
- Suitable for complex programming structures
- Easy to maintain: FBD block diagrams are easy to read and analyze, helping to quickly identify and fix errors in the system.
Disadvantages
- Memory Occupancy: Due to the graphical nature of FBD, programs can take up more memory than programming languages such as Instruction List (IL) or Structured Text (ST).
- Limited function blocks: Although there are many standard function blocks, sometimes building a custom block is more complex than programming in text languages such as ST.
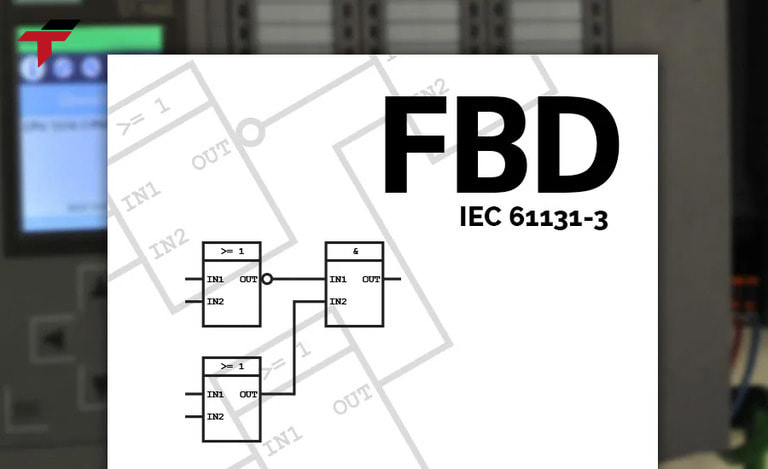
This is a function block diagram – a widely used programming language
Instruction List (IL)
This is the first PLC programming language, and it is a text-based programming language. It is a low-level language because when you use it, you will work with codes, components like LD, AND, OR…
The language look like assembly. But this language can be very compatible with hardware of PLC which can provide very high speed than other language and by that it use in professional cases like fast calculation and fast take action.
Advantages
- High standardization: The language requires users to follow a clear structure, from declaring variables, defining conditions, to listing detailed instructions.
- Command-oriented: Focus on processing instructions instead of managing data flow.
- Memory saving: Due to concise syntax, IL programs often take up less memory than other programming languages such as Ladder Diagram (LD) or Function Block Diagram (FBD).
Disadvantages
- Difficult to maintain: Programs written in IL are often harder to read and follow, especially for large projects or when handing over to others.
- Hard to detect errors: Because the syntax is close to machine code, small errors in the code (such as syntax errors or wrong commands) can have a large impact and are difficult to detect.
- Limitations on most PLC platforms

This is the first PLC programming language, and it is a text-based programming language
What Are the Benefits of Using Different PLC Programming Languages?
Using the appropriate PLC programming language can bring multiple advantages to automation projects, improving both development and operational performance.
- Flexibility and Scalability of Automation Projects: Different PLC languages allow engineers to choose the most suitable tool for each specific task. Visual languages like Ladder Diagram (LD) or Function Block Diagram (FBD) are ideal for straightforward control, while Structured Text (ST) can handle complex calculations.
- Faster Debugging and Maintenance: Choosing the right language can simplify troubleshooting and reduce downtime. Visual programming languages provide intuitive diagrams that are easy to read and debug, while structured languages allow precise control over logic, making maintenance faster and more efficient.
- Improved Efficiency and Productivity in Industrial Processes: Using the optimal language for each task ensures that automation systems operate smoothly and efficiently. Processes run more reliably, errors are minimized, and production output is maximized, ultimately improving overall industrial productivity.
How to Choose the Right PLC Programming Language?
Selecting the right PLC programming language is essential for project efficiency and long-term maintainability. Key factors to consider include:
- Project Complexity: Simple tasks work well with visual languages like Ladder Diagram (LD), while complex logic or calculations may require Structured Text (ST).
- Hardware Compatibility: Ensure the language is supported by your PLC brand or model to avoid integration issues.
- Team Expertise: Choose a language that matches your team’s skills to reduce errors and speed up development.
- Standardization (IEC 61131-3): Using standard languages ensures portability, easier maintenance, and compatibility across systems.
- Application Needs: Certain tasks like sequential operations or motion control may perform better with SFC, FBD, or CFC.
By evaluating these factors, you can select the most suitable PLC language for your project, ensuring reliable and efficient automation.
Conclusion
Choosing the right PLC programming language is a crucial step for ensuring efficient, reliable, and maintainable automation systems. Each language—whether Ladder Diagram, Function Block Diagram, Structured Text, Sequential Function Chart, or Continuous Function Chart—offers unique advantages and is suited to specific types of industrial processes.
At Flextech, we specialize in providing comprehensive PLC solutions and automation services tailored to your industry needs. Our team of experts can help you select the right programming language, design robust control systems, and implement efficient automation strategies.


