A Remote Terminal Unit (RTU), also known as a remote terminal device, is a specialized micro-processor-based unit designed to collect, monitor, and control industrial devices and machinery from a substantial distance. RTUs are essential components in automation and control systems, acting as a crucial interface between physical field devices and a central monitoring system.
Thanks to their stable operation and ability to monitor and manage processes remotely, RTUs are widely deployed across various critical sectors. They are most commonly encountered in smart grid devices, oil and gas production areas, and wastewater treatment plants.
By the end of this article, you will have a comprehensive understanding of the functions, core components, key advantages, and specific applications of this powerful device.
What are the Outstanding Functions of an RTU?
The RTU remote terminal unit performs several outstanding functions that are vital for effective industrial automation and process control:
- Data Monitoring and Collection: The RTU’s primary function is to constantly collect and monitor data from various sensors and gauges connected in the field. This collected data includes critical operational parameters such as temperature, liquid level, flow rate, speed, device location, and equipment security status.
- Data Transmission: The RTU compiles the vast amount of raw information received from the field devices, standardizes it, and transmits it efficiently to the central control system (often a SCADA system) for comprehensive process management and control.
- Remote Management and Control: RTUs support real-time remote monitoring and execution of control commands on field devices. This capability helps organizations significantly increase productivity, reduce system downtime, and optimize operating costs across the entire operation.
- Wide Application and Technological Advancement: Incorporating advanced technologies, such as microprocessors, the modern RTU is trusted and widely used across numerous industrial and commercial applications, including power generation, utility distribution (water and gas), and building automation systems.
What are the Outstanding Functions of an RTU?
Where is the RTU Commonly Used?
Due to their effectiveness in data collection, management, and real-time monitoring, RTUs are essential in many high-demand industrial environments:
- Smart Grids: RTUs are integral to modern power distribution networks. They monitor and control electricity flow, ensuring real-time management of power to households and businesses with the required voltage level, optimizing network stability and reliability.
- Oil and Gas Production: In this sector, RTUs monitor critical infrastructure such as pipelines for leaks, tank levels at storage facilities, and wellhead status. This remote capability is key to facilitating more efficient and safe oil and gas production processes.
- Water and Wastewater Treatment: RTUs are crucial for maintaining water quality and plant efficiency. They help monitor and control vital parameters like the water or wastewater treatment plants’ pH, flow rate, or the precise levels of chemical dosage.
- Alternative Energy Systems: They are used to control and monitor the performance of renewable energy systems, including solar panel arrays, wind turbines, or hydroelectric plants, ensuring stable energy performance and providing immediate warnings for anomalies.
- Remote Measurement Systems: RTUs enable the remote monitoring and control of equipment located in isolated or hazardous areas, such as offshore oil rigs and remote weather stations. This provides optimal convenience and ensures maximum safety for operators.
What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of an RTU?
Like any specialized device, the Remote Terminal Unit offers a distinct set of benefits and limitations:
Advantages
- Low Power Consumption: RTUs are highly suitable for remote locations where the power supply may be limited. They are designed to be energy-efficient, often prioritizing data transmission only when necessary, which conserves power.
- Durable Operation in Harsh Environments: These devices are built to be highly durable and robust. They can withstand harsh weather and difficult industrial conditions, making them ideal for deployment in remote or challenging environments like mountainous areas.
- Automatic Data Storage: RTUs can store data from their I/O devices with accurate time and date stamps. This stored data can be transmitted reliably when communication is restored, even after periods of unstable communication.
- Highly Customizable and Flexible: RTUs offer significant flexibility. They can be easily expanded and customized with various communication modules, I/O cards, data storage options, and backup power supplies/batteries to meet specific application needs.
Disadvantages
- High Installation and Maintenance Cost: The initial investment for installing and maintaining a complete RTU system can be substantial, with the typical cost of a comprehensive RTU device being around $1,100 or more.
- Potential for Outdated Technology: Some older RTU models may utilize legacy technology, resulting in slower data processing speeds compared to more modern control systems. Careful consideration is required to select an RTU that meets current operational demands.
- Limited Processing Power: Relative to specialized industrial computers or Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), the RTU has limitations in terms of advanced data processing and complex storage capabilities. This can restrict its use in certain high-demand, high-computation applications.
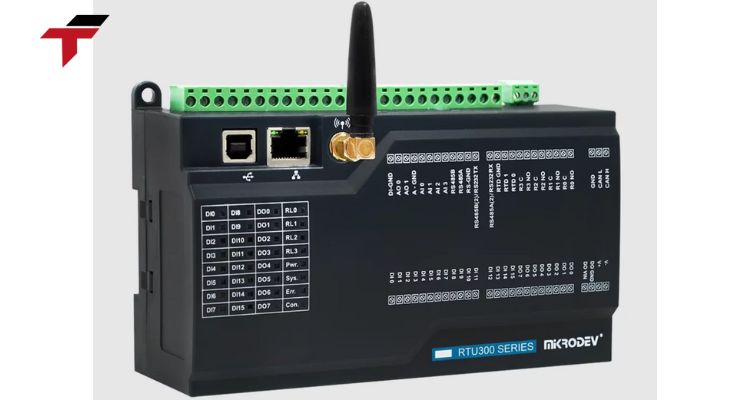

What are the Advantages and Disadvantages of an RTU?
What are the Basic Components of an RTU Device?
A basic RTU is designed around a set of core hardware components that enable its functionality:
- Central Processor (CPU): This is the “brain” of the unit. It supports the processing of main data and possesses programming capabilities, similar to a PLC, typically utilizing a 32-bit microprocessor. In modern units, configuration is often managed through a basic web interface.
- Power Source: Most RTUs are powered by the main electrical grid. They almost always include a robust backup battery to ensure continuous operation in remote locations or during unexpected power failures.
- Communication Port: This port is essential for connecting the RTU to the central SCADA or control system. It facilitates data exchange using industrial communication protocols such as Ethernet, RS-232, or Modbus.
- Physical I/O (Input/Output): These are the interface modules that connect directly to field devices. They include digital and analog input modules (for collecting data) and output modules (for sending control commands) to devices in the field.
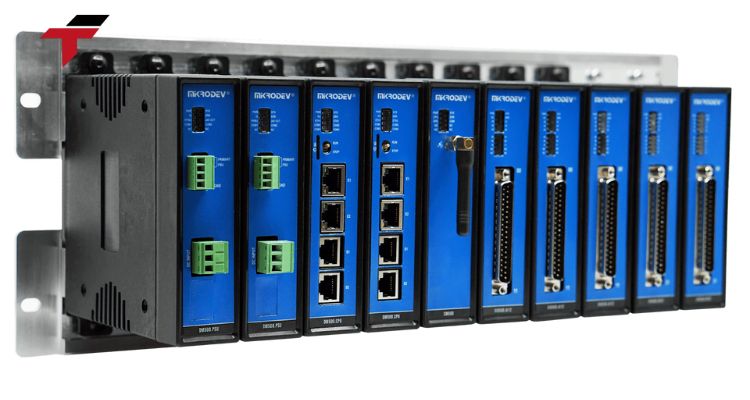

What are the Basic Components of an RTU Device?
How is RTU Different from SCADA?
The RTU and SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) systems are fundamentally linked but serve distinct roles in the overall control architecture:
| Feature | RTU (Remote Terminal Unit) | SCADA (Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition) |
| Nature | A hardware device that collects data and performs basic control actions. | A specialized software system for monitoring, control, and data analysis. |
| Primary Function | To collect data and execute control commands locally at the field site. | To process, display, and manage data; popular in monitoring, alarming, and high-level decision-making. |
| Cost | More affordable, primarily a hardware investment. | Higher cost due to the integration of complex features and specialized software. |
| User Interface | Primarily a hardware assembly; does not integrate a human-machine interface (HMI). | Primarily a software system; includes an HMI to provide visual information and operator control. |
| Connection | Connects to the central SCADA system via communication protocols (e.g., Modbus, DNP3). | Communicates with one or many RTUs, storing and processing the collected data for accurate control. |
In short, the RTU is the intelligent field device that acts on physical equipment, while SCADA is the central software platform that supervises, analyzes, and directs the entire automated system.


