The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the heart of any PLC system, responsible for processing data, executing control logic, and communicating with connected devices. Understanding the CPU’s role is essential for designing efficient, reliable, and high-performing automation systems in modern industrial environments.
History of CPU in PLC industry
In the field of PLC, CPUs were developed in parallel with the birth of PLC in 1968 by Modicon (now part of Schneider Electric). Initially, PLC CPUs only performed simple tasks such as replacing mechanical relays. However, with the development of microprocessor technology, CPUs in PLCs have become increasingly powerful, capable of processing data faster, supporting multiple communication protocols, and ensuring high reliability in harsh industrial environments.
The continuous advancement of CPUs has contributed significantly to promoting industrial automation, bringing production lines and factories into the intelligent era.
What Is a Central Processing Unit (CPU)?
The Central Processing Unit (CPU), often referred to as the “brain” of a computer or industrial control system, is the primary component responsible for executing instructions and managing operations. It processes data, interprets commands from software, and coordinates the activities of all other system components. In essence, the CPU controls how information flows between memory, input/output devices, and other hardware, ensuring that tasks are performed efficiently and accurately.
A CPU consists of several key components:
- Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU): Performs mathematical calculations and logical operations.
- Control Unit (CU): Directs the flow of data and instructions within the CPU and coordinates with other system components.
- Registers: Small, high-speed storage locations that temporarily hold data, instructions, or addresses during processing.
In industrial automation, CPUs are integral to devices such as Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs), HMIs, and embedded systems, where they execute control algorithms, monitor sensors, and manage actuators to ensure smooth and precise operations.

The Central Processing Unit (CPU), often referred to as the “brain” of a computer or industrial control system
How many parts does a CPU consist of?
The CPU consists of the following 3 main components: Processor, Memory, Communication Interface:
Processor
This is where all the calculation and logic processing takes place. The microprocessor performs logical operations, controls the flow of data, and makes decisions based on the programmed program. The speed of the microprocessor determines the performance and response time of the PLC.
Memory
Memory is an important component of the CPU, where programs, data and system status information are stored. Memory is divided into three main types:
- ROM (Read-Only Memory): Stores PLC firmware – core programs needed for the system to operate.
- RAM (Random Access Memory): Stores temporary data while the CPU is processing. Data in RAM will be lost when the power is turned off.
- EEPROM/Flash Memory: Stores user-programmed programs, helping to protect data even when the power is lost.
Communication Interface
The CPU needs to communicate with other devices in the system such as SCADA, HMI, or expansion modules through communication ports such as Ethernet, Modbus, Profibus. These interfaces allow the CPU to receive input data and send control information to the output.
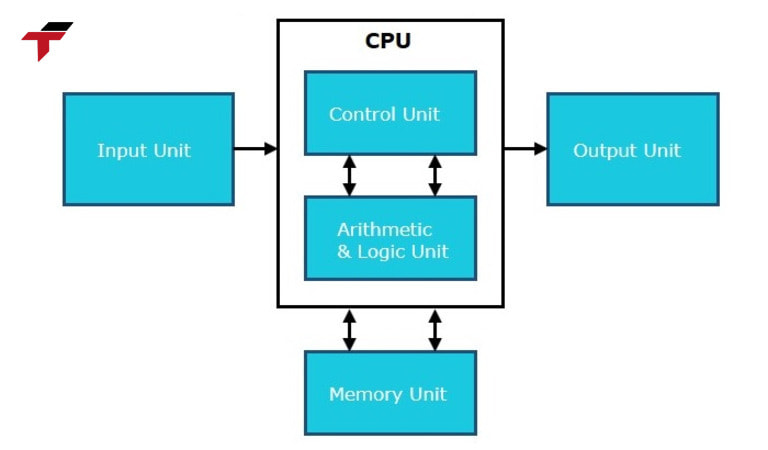
The CPU consists of the following 3 main components: Processor, Memory, Communication Interface
How Does a CPU Interact with Other System Components?
The CPU serves as the brain of a system, coordinating operations between memory, input/output devices, and other components. Its interactions can be understood in several key ways:
- Communication with Memory: The CPU reads instructions and data from RAM or cache, processes them, and writes results back to memory. This interaction allows programs to execute efficiently and supports multitasking.
- Coordination with Input/Output (I/O) Devices: The CPU sends control signals to I/O devices to perform actions, such as reading sensor data or controlling actuators. It also receives data from input devices to process and respond accordingly.
- Integration with Buses: The CPU uses data, address, and control buses to exchange information with other components. These buses ensure synchronized and fast data transfer across the system.
- Interaction with Co-processors and Peripherals: Specialized co-processors, such as GPUs or digital signal processors, work alongside the CPU to handle specific tasks efficiently. The CPU manages overall coordination while offloading complex calculations to these units.
Through these interactions, the CPU ensures the system operates seamlessly, executing programs accurately and controlling industrial or computing processes in real time.
What Are the Main Functions of a CPU in a PLC?
CPU in PLC plays a central role, ensuring that the entire system operates accurately and efficiently. To perform the task of “running a process”, the CPU must complete a series of closely linked tasks:
- Communicate with the programming machine and download the program connects to the programming machine (laptop or PC) to receive the control program. During this process, the CPU downloads the instructions from the programming machine and stores them in memory for execution.
- Backplane I/O Data Transfer: The CPU manages the data transfer between input/output modules via the backplane. This is an internal connection in the PLC that ensures that data moves quickly and accurately between components.
- Read and update Input Registers: The CPU scans the status of all input signals from sensors or switches and stores them in the input registers. This information is then used to calculate the control logic.
- Logic Execution: The CPU processes each line of code in the program in order, performing arithmetic and logic operations to determine what action to take. This is an important step for the CPU to convert input data into control instructions.
- Updating the Output Registers: After processing the logic, the CPU updates the output register, which contains control instructions to send to devices such as motors, valves, or indicator lights. These instructions are transmitted to the output modules for execution.
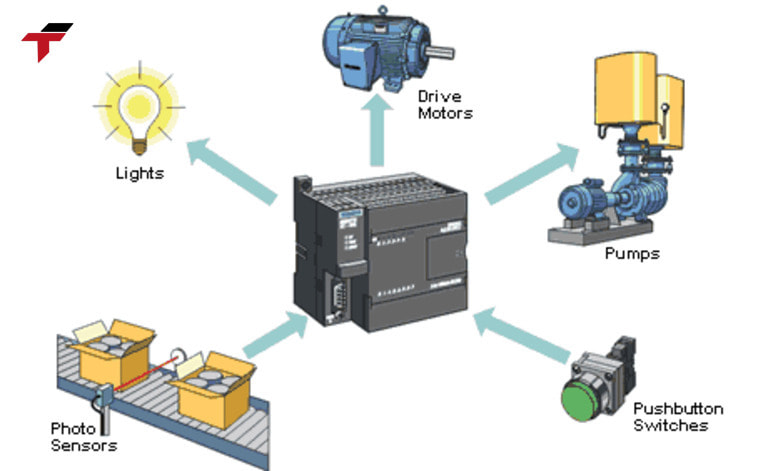
CPU in PLC plays a central role
What are the important things to consider when choosing a CPU?
Choosing the right CPU not only ensures the system operates efficiently but also saves costs and increases operational reliability. Here are 5 things you need to consider before choosing a CPU for your PLC system:
- Suitable communication protocol: For systems that use laptops for programming, make sure the CPU is compatible with the communication protocol of the programming device.
- Memory capacity: The CPU’s memory must be large enough to store the entire control program as well as the necessary data. For small production processes, a CPU with less than 100 MB of memory is usually sufficient. However, to be sure, you should discuss directly with the manufacturer or supplier to make the right choice based on the specific requirements of the system.
- Number of Input/Output: Each CPU is designed to support a certain number of I/O points. If the system has more devices than the CPU can support, choose a CPU that supports I/O module expansion.
- Brand: Choose CPUs from reputable manufacturers such as Siemens, Rockwell Automation, Mitsubishi, Schneider Electric.
- Cost: Consider the cost of purchasing the CPU and related costs such as expansion modules, programming software, and maintenance. Prices range from $2000 – $3000

Here are 5 things you need to consider before choosing a CPU for your PLC system
Conclusion
The Central Processing Unit (CPU) is the brain of any PLC system, coordinating data processing, executing control logic, and ensuring smooth communication with all connected devices. Choosing a high-performance CPU tailored to your industrial needs can significantly improve automation efficiency, reliability, and overall system performance.
At Flextech, we provide advanced PLC solutions, including high-quality CPUs and complete automation systems, designed to help businesses optimize processes, reduce downtime, and achieve higher productivity in the era of smart manufacturing.


